Journal Description
Disabilities
Disabilities
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the physical, biopsychosocial, and environmental aspects of disability, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 41.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Health Professions (miscellaneous))
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Factors Influencing the College Decision-Making Process for Students with Disabilities
Disabilities 2025, 5(2), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5020036 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to increase understanding of the college decision-making process for students with disabilities by listening to their perceptions of factors that influenced their decisions related to attending postsecondary education. A semi-structured interview was used to provide descriptive evidence
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this study is to increase understanding of the college decision-making process for students with disabilities by listening to their perceptions of factors that influenced their decisions related to attending postsecondary education. A semi-structured interview was used to provide descriptive evidence from 20 college-going high school students with disabilities. Content analysis was utilized to evaluate the data collected. The results suggest that the factors influencing the college decision-making process of students without disabilities also influence the decision-making process of students with disabilities.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Barriers and Facilitators in Reaching and Supporting Parents with Intellectual Disabilities
by
Maroesjka Van Nieuwenhuijzen, Sanna Koet and Marcia Lever
Disabilities 2025, 5(2), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5020035 - 31 Mar 2025
Abstract
Support of parents with intellectual disabilities should be long-term and start as early as possible. They, however, often come only into view late. The aim of the present study was to examine the barriers and facilitators in reaching and supporting parents with intellectual
[...] Read more.
Support of parents with intellectual disabilities should be long-term and start as early as possible. They, however, often come only into view late. The aim of the present study was to examine the barriers and facilitators in reaching and supporting parents with intellectual disabilities and young children in the Netherlands. Fourteen professionals, three volunteers, and three mothers with intellectual disabilities participated in four focus groups. Results revealed four themes: (1) improve professional development, (2) mutual professional/parent distrust, (3) strengthen support network systems, and (4) improve child welfare system responses. Professionals and policymakers lack knowledge of parents with intellectual disabilities and skills to build trust and support them adequately. Professional development is warranted. The informal network and involvement of fathers is limited and, thus, could be increased. Finally, the way the system is organized impedes adequate support. Long-term involvement and, thus, a different use of resources is needed. Reaching parents with intellectual disabilities as early as possible is important but challenging due to multiple interacting factors. Integral actions at multiple levels are essential to improve preventive care for these parents.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Improving the Socio-Vocational Skills of Adults with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Using Video Modeling: A Pilot Study
by
Yfat Ben Refael, Patrice L. Weiss, Yael Shidlovsky Press, Eynat Gal and Sharon Zlotnik
Disabilities 2025, 5(2), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5020034 - 26 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In today’s job market, effective social communication is crucial for employment success. We investigated “Cog ‘n’ Role”, a novel video modeling (VM) intervention that integrates video self-modeling (VSM) and social problem-solving therapy (SPST) to enhance socio-vocational skills in individuals with intellectual and developmental
[...] Read more.
In today’s job market, effective social communication is crucial for employment success. We investigated “Cog ‘n’ Role”, a novel video modeling (VM) intervention that integrates video self-modeling (VSM) and social problem-solving therapy (SPST) to enhance socio-vocational skills in individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDDs). The intervention is delivered via “PowerMod”, an application featuring ready-to-use VM scenarios and enhanced accessibility options; our aim was to examine (a) the app’s social validity and (b) the effectiveness of the intervention in improving job-related social skills. Thirty-four adults with IDD used “PowerMod” to view video clips of common workplace scenarios and rated their experiences through questionnaires. Subsequently, seventeen adults who have social difficulties at work participated in four weekly therapy sessions featuring the “Cog ‘n’ Role” intervention via the PowerMod app. Socio-vocational skills were measured through questionnaires filled out by their counselors; participants found the adapted video clips to be significantly more comprehensible and relevant compared to non-adapted video clips. Additionally, the intervention group showed significant improvements in socio-vocational behaviors and a significant transition to jobs that required higher levels of independence. These findings provide preliminary evidence for the impact of this innovative intervention in enhancing socio-vocational skills among individuals with mild to moderate IDD.
Full article
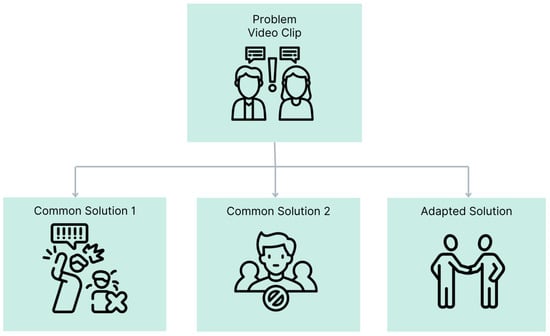
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
A Systematic Review of Volunteer Motivation and Satisfaction in Disability Sports Organizations
by
Antonio Muñoz-Llerena, Salvador Angosto, Carlos Pérez-Campos and Virginia Alcaraz-Rodríguez
Disabilities 2025, 5(2), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5020033 - 21 Mar 2025
Abstract
Volunteering in sports for people with disabilities is a crucial element for social inclusion and development. Therefore, this systematic review aims to analyze the existing literature on the motivation, satisfaction, engagement, and commitment of volunteers in sports for people with disabilities. Following PRISMA
[...] Read more.
Volunteering in sports for people with disabilities is a crucial element for social inclusion and development. Therefore, this systematic review aims to analyze the existing literature on the motivation, satisfaction, engagement, and commitment of volunteers in sports for people with disabilities. Following PRISMA guidelines, a comprehensive search was conducted across four databases, the Web of Science, Scopus, PsycInfo, and SportDiscus, resulting in the inclusion of 16 studies. The geographic distribution showed the existence of studies on all continents, particularly in Europe and Asia, and most studies were quantitative. The findings revealed that volunteer motivation was predominantly intrinsic, driven by values, understanding, and personal growth, with less emphasis on extrinsic factors such as career advancement. Satisfaction levels were generally high, particularly among student volunteers, who also showed strong future intentions to continue volunteering. As a conclusion, there was a limited number of studies exclusively focused on volunteers participating in sports for people with disabilities. This review highlights the need for more research on diverse types of disabilities and the development of inclusive policies and training programs to enhance volunteer experiences. The study underscores the importance of recognizing both personal and professional motivators to effectively recruit and retain volunteers in sports organizations supporting people with disabilities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Leisure and Sport Activities among People with Disabilities: Opportunities and Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures
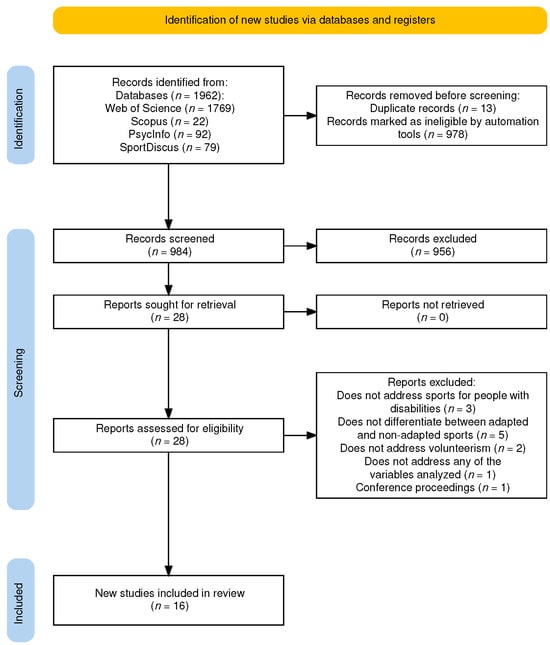
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Children Suspected for Developmental Coordination Disorder in Hong Kong and Associated Health-Related Functioning: A Survey Study
by
Kathlynne F. Eguia, Sum Kwing Cheung, Kevin K. H. Chung and Catherine M. Capio
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010032 - 18 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Children with developmental coordination disorder (DCD) have motor difficulties that interfere with their daily functions. The extent to which DCD affects children in Hong Kong has not been established. In this study, we aimed to estimate the prevalence of children suspected of DCD
[...] Read more.
Children with developmental coordination disorder (DCD) have motor difficulties that interfere with their daily functions. The extent to which DCD affects children in Hong Kong has not been established. In this study, we aimed to estimate the prevalence of children suspected of DCD (sDCD) in Hong Kong and to examine the relationship between motor performance difficulties and health-related functioning. We conducted a cross-sectional survey of parents of children aged 5 to 12 years across Hong Kong (N = 656). The survey consisted of the Developmental Coordination Disorder Questionnaire (DCDQ) and short forms on global health, physical activity, positive affect, and cognitive function of the Patient-Reported Outcome Measurement Information System (PROMIS®) parent-proxy report scales. We found that the total DCDQ score categorized 18.29% of the children as sDCD. Logistic regression revealed that household income (OR 0.776, p < 0.001) and child age (OR 1.012, p = 0.004) contributed to being categorized as sDCD. Children categorized as sDCD had lower global health (p < 0.001), less positive affect (p < 0.001), and more impaired cognitive function (p < 0.001) than children categorized as probably not DCD (nDCD). The findings of this study contribute to clarifying the extent to which DCD might affect Hong Kong children and serve as a basis to advocate for programs that address motor, health, affective, and cognitive outcomes. Further research is recommended to estimate the prevalence of a DCD diagnosis in Hong Kong.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Everyday Assistive Products Support Participation in Sport
by
Ana Geppert, Emma M. Smith and Malcolm MacLachlan
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010031 - 17 Mar 2025
Abstract
The benefits of participation in sport are widespread, and include not only improved health and wellness, but also support social participation and the realization of rights. Research on the use of assistive products in sport participation has previously focused largely on the use
[...] Read more.
The benefits of participation in sport are widespread, and include not only improved health and wellness, but also support social participation and the realization of rights. Research on the use of assistive products in sport participation has previously focused largely on the use of specialized products in elite sport and has not addressed the importance of everyday assistive products for facilitating sport participation. This research aims to highlight the use of the 50 products on the World Health Organization’s Priority Assistive Product List for sport participation. We found that all 50 products are relevant to sport participation, and support participants to engage directly in sport, but also in social engagement with other sport participants, and as observers and fans of sport.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Leisure and Sport Activities among People with Disabilities: Opportunities and Challenges)
Open AccessArticle
Developmental Language Disorder at Adolescence: Links Between Communication Skills and Self-Efficacy Ratings
by
Anabel Buteau-Poulin, Nancy Gaudreau and Chantal Desmarais
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010030 - 14 Mar 2025
Abstract
Developmental Language Disorder (DLD) has a prevalence of 7%, making it one of the important yet little known neurodevelopmental disorders. Often identified in kindergarten, children with DLD have language learning difficulties severe enough to impact their schooling and socialization. During adolescence, there is
[...] Read more.
Developmental Language Disorder (DLD) has a prevalence of 7%, making it one of the important yet little known neurodevelopmental disorders. Often identified in kindergarten, children with DLD have language learning difficulties severe enough to impact their schooling and socialization. During adolescence, there is a high risk of academic, vocational, and mental health difficulties. However, for adults with DLD, a positive perception of self-efficacy may act as a protective factor. This led us to explore how communications skills and self-efficacy are related in adolescents with DLD. The participants were 49 teenagers, aged 12 to 15, who have DLD. Communication was measured using the Children’s Communication Checklist, completed by the teenagers’ parents, while perception of self-efficacy was reported by the teenagers as well as by their parents using the Generalized Self-Efficacy Scale. A significant correlation was found between communication and self-efficacy with three domains of communication being the most important in this association, i.e., coherence (r = 0.716, p < 0.001), initiation (r = 0.581, p < 0.001), and use of context (r = 0.649, p < 0.001). These results highlight the crucial role of social communication in the profile of teenagers living with DLD. They further suggest that it may be relevant to examine whether supporting language development may foster positive perception of self-efficacy in teenagers living with DLD.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Biological or Prosthetic Limb—Which Is More Advantageous for Running Performance? A Narrative Review
by
Derek W. Elton, Mackenzie Minter and Feng Yang
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010029 - 13 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As the field of prosthetic engineering advances, questions around whether these new prosthetics hold the ability to outperform biological limbs become more relevant. To further clarify such a debate and discover gaps in our understanding, a narrative review of the present literature on
[...] Read more.
As the field of prosthetic engineering advances, questions around whether these new prosthetics hold the ability to outperform biological limbs become more relevant. To further clarify such a debate and discover gaps in our understanding, a narrative review of the present literature on this topic is needed. The purpose of the present review was to explore whether prosthetic legs grant amputee athletes an unfair advantage over traditional athletes by reviewing 11 articles pertaining to the running performance and potential among athletes with transtibial amputations. The findings of the included articles were categorized into three domains of running performance, chosen due to their precedence in the current literature: propulsion forward, limb repositioning, and physiological limitations. Our review indicated that the present literature alludes to transtibial amputee runners having a potential competitive advantage over able-bodied runners, with the caveat that some performance domains appear not to be differentiated. The present findings offer a unique perspective on understanding the impact of prosthetics on the running performance among para-athletes and suggest future research directions. As the depth of this area of literature increases, future systematic reviews and meta-analyses may be able to answer with greater certainty whether transtibial prosthetics allow for supra-biological running performances.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
We’re Moving Online: Lessons Learned During the COVID-19 Pandemic to Support Adaptive Leisure Time Physical Activity in the Virtual Environment
by
Cassandra Herman, Delphine Labbé and Chelsea Elder
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010028 - 12 Mar 2025
Abstract
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, people with disabilities were particularly inactive and online programs offered new opportunities for their engagement in leisure time physical activity (LTPA). However, research regarding how virtual adaptive LTPA programs were developed and delivered is limited. This case study examined
[...] Read more.
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, people with disabilities were particularly inactive and online programs offered new opportunities for their engagement in leisure time physical activity (LTPA). However, research regarding how virtual adaptive LTPA programs were developed and delivered is limited. This case study examined the staff perceptions of developing and delivering virtual adaptive LTPA for people with disabilities to better understand the barriers and facilitators organizations experienced during its implementation. Five semi-structured interviews conducted with staff of a community-based organization specializing in adaptive LTPA explored the process of transitioning to a virtual format, challenges and facilitators, and lessons learned. Interviews were analyzed using inductive content analysis and organized around three themes. Systematic development of virtual programs suggested that supporting the organization, staff and members facilitates virtual adaptive LTPA. Creativity and resourcefulness in delivering programs highlighted the importance of flexible management and using staff skills. Effects of transitioning to virtual programming emphasized positive impacts of virtual LTPA such as connectedness, health benefits, and expanded organizational reach. The results of this study emphasize the benefits of virtual adaptive LTPA and highlight key management factors that organizations can use to provide virtual opportunities for adaptive LTPA for people with disabilities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Leisure and Sport Activities among People with Disabilities: Opportunities and Challenges)
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Participative Environments of Children with Learning and Physical Disabilities: Perspectives from Parents and Practitioners
by
Anu Kinnunen and Leena Holopainen
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010027 - 10 Mar 2025
Abstract
It is unclear how parents and professionals working together can create environments that enhance the functioning and participation of children with disabilities. This study investigates parents’ and practitioners’ conceptions of the environmental factors and collaboration that support the participation of children with learning
[...] Read more.
It is unclear how parents and professionals working together can create environments that enhance the functioning and participation of children with disabilities. This study investigates parents’ and practitioners’ conceptions of the environmental factors and collaboration that support the participation of children with learning and physical disabilities. The data were collected from children’s parents, therapists, and teachers (N = 10) through focus group discussions. The data were analyzed using qualitative content analysis based on an inductive approach. Various physical, psychological, and social barriers, along with a lack of collaboration in the child’s environment, were found to prevent the child’s full participation. Linking children’s therapy to everyday activities and learning was found to be the best way to improve children’s functioning and participation in all the environments studied. Adult collaboration based on a child-oriented approach was perceived as essential for enhancing the children’s functioning and participation and for fostering inclusion in school and everyday life.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Co-Designing Tiyanjane, a Participatory Intervention to Promote Parental Involvement in the Education of Children with Disabilities in Malawi
by
David John Musendo, Blessings Chirwa, Chisomo Kamata, Daksha Patel, Tracey Smythe and Sarah Polack
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010026 - 3 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper describes the co-design of a participatory group intervention developed to promote and enhance parental involvement in supporting the education of children with disabilities in Malawi. The intervention was developed through participatory co-design workshops and consensus meetings involving 23 stakeholders, including parents,
[...] Read more.
This paper describes the co-design of a participatory group intervention developed to promote and enhance parental involvement in supporting the education of children with disabilities in Malawi. The intervention was developed through participatory co-design workshops and consensus meetings involving 23 stakeholders, including parents, teachers, and community leaders. The Behaviour Change Wheel framework and the Delphi technique guided the intervention development process, ensuring theoretical robustness and contextual relevance. The proposed intervention, Tiyanjane (‘Let Us Unite’), includes facilitator and participant training and practical face-to-face sessions over 12 weeks. The intervention targets four key areas: developing family action plans, holding regular meetings, providing ongoing support at home and school, and facilitating training and information exchange. This participatory approach, involving a wide range of local stakeholders, offers valuable insights into the process and outcomes of co-developing culturally relevant and theoretically grounded interventions to address the needs of families with children with disabilities in low-resource settings. Future research should include an evaluation of the feasibility and acceptability of the intervention and examine its applicability in diverse sociocultural settings within LMICs (low- and middle-income countries).
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Child Enjoyment and Parental Satisfaction with Autistic Children’s Participation in Active and Sedentary Activity Configurations
by
Danielle Salters, Samiya Sheiknur and Sara M. Scharoun Benson
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010025 - 28 Feb 2025
Abstract
This research used proxy reports and questionnaire-based data to explore characteristics related to participation among autistic children. The research aimed to explore child enjoyment and parental satisfaction in different activity configurations, including active and sedentary pursuits and activities in which children participate alone
[...] Read more.
This research used proxy reports and questionnaire-based data to explore characteristics related to participation among autistic children. The research aimed to explore child enjoyment and parental satisfaction in different activity configurations, including active and sedentary pursuits and activities in which children participate alone or in groups. Parents/guardians (n = 100) of autistic children aged 4–15 years completed questionnaire-based assessments of their autistic child’s motor skills, social skills, and characteristics of participation. Regression analyses were completed to elucidate the factors that may contribute to a child’s enjoyment of and parental satisfaction with the child’s participation in the different activity configurations. A strong positive correlation was found between motor and social skills, and for motor and social skills in concert with the different activity configurations. Regression analyses found that the social skills of autistic children were related to participation in most of the activity configurations for both the child’s enjoyment and parental satisfaction in participation. Other results indicated that lower social skills were more strongly related to child enjoyment and parental satisfaction, and that the highest enjoyment and satisfaction scores were found for the sedentary and individual activities. These results reinforce the impact of social skills on participation in various activities, and the need for early intervention to promote skill development among autistic children.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Perceptions of Stigma and Social Inclusion Amongst a Sample of University Students with ADHD in Ireland
by
Sorcha Smith and Joanne McVeigh
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010024 - 26 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurological disorder generally experienced as challenging, as it impacts multiple aspects of an individual’s life. There is a significant gap in the literature surrounding ADHD in adults, including experiences of stigma and social inclusion from the
[...] Read more.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurological disorder generally experienced as challenging, as it impacts multiple aspects of an individual’s life. There is a significant gap in the literature surrounding ADHD in adults, including experiences of stigma and social inclusion from the perspective of people with ADHD. This study aimed to explore perceptions and experiences of social inclusion and stigma amongst a sample of university students with ADHD living in Ireland. Nine semi-structured interviews were conducted with seven participants (four men and three women), including two follow-up interviews. The participants were all university students with an official diagnosis of ADHD. Data from the interviews were analysed using the descriptive and interpretive method of Constant Comparison Analysis. In total, sixteen categories (themes) were extracted and classified into five overarching domains: informational access, access to healthcare, attitudinal access, social inclusion, and academic accommodations. The findings indicated that ADHD adversely affects university students’ experience of social inclusion. Barriers to effective healthcare, negative attitudes towards ADHD, and misinformation/lack of information were all highlighted as risk factors for feelings of social exclusion. Universities should include students with disabilities when designing policies and provide accommodations to support them. Additionally, greater awareness and informational access is imperative to improving social inclusion for people with ADHD.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Current Roles of Support Teachers, Analysis of Their Contribution to Inclusive School: A Narrative Review
by
Lara Astudillo, Cecilia Simón and Maria Luz M. Fernández Blázquez
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010023 - 25 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Support in the context of inclusive education is pivotal, yet many countries struggle with integrating the evolving role of support teachers within inclusive frameworks. For that reason, some challenges and reluctance can be found in relation to the development of the functions of
[...] Read more.
Support in the context of inclusive education is pivotal, yet many countries struggle with integrating the evolving role of support teachers within inclusive frameworks. For that reason, some challenges and reluctance can be found in relation to the development of the functions of these professionals. Therefore, a way forward would be to clarify the role and responsibilities of support teachers in fostering inclusive educational environments. This paper aims to contribute to this discourse by conducting a narrative review of existing research on the functions of support teachers. Special attention is paid to their contributions in the construction of inclusive educational contexts. The review, which was inspired by the guidelines of the PRISMA statement, yielded 23 final studies. Four professional roles were identified: direct care-assistance, consultative-collaborative, administrative-documentary, and coordinator-leadership. Furthermore, the findings indicate that there is a predominance of individual or small group support practices outside the regular classrooms. The need to implement collaborative practices to generate support networks at both school and community levels is emphasized. Three major themes were identified as the primary challenges: teacher training, collaboration among educators, and school curricula, particularly in the post-primary stages. Orientations for rethinking the role of support teachers from an inclusive approach are outlined in the discussion.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Can Systematic Justice Be Achieved for Parents with Intellectual Disabilities in Deprivation of Custody Cases?
by
Hanna Björg Sigurjónsdóttir and James Gordon Rice
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010022 - 23 Feb 2025
Abstract
This case report is a reflection on the cumulative results of a number of research projects conducted in Iceland in the field of parenting with a disability. The underlying research consisted primarily of an analysis of court case documents and interviews with parents,
[...] Read more.
This case report is a reflection on the cumulative results of a number of research projects conducted in Iceland in the field of parenting with a disability. The underlying research consisted primarily of an analysis of court case documents and interviews with parents, extended family members and relevant professionals. The contribution that follows emerged out of a question that we posed to our overall research findings and experiences—what does justice look like for parents with ID who have to contend with deprivation of custody orders? In the rare instances in which a parent ultimately prevailed over an unjust deprivation order, this was only accomplished after an extensive fight through the court system, after which, a great deal of harm to the family had already been caused. We offer for consideration a close look at one such case that we followed, the aftereffects of which are still ongoing. The other path to success appears to be that of early intervention, but this typically occurs through happenstance and requires the involvement of a network of progressive professionals and fortuitous timing. Our contribution is a call to discuss what justice looks like and how this may be transformed into something more systematic.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Barriers and Facilitators to Initial and Ongoing Implementation of Community-Based Exercise Programs for Persons with Physical Disabilities: Qualitative Perspectives of Program Providers
by
Kristiann E. Man, Olivia Varkul, Lauren Konikoff, Natasha Bruno, Marlee Konikoff, Yetnayet Sisay Yehuala, Amy E. Latimer-Cheung and Jennifer R. Tomasone
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010021 - 22 Feb 2025
Abstract
Community-based exercise programs (CBEPs) designed for persons with physical disabilities can promote participation in physical activity (PA). Despite their importance, few CBEPs for persons with physical disabilities exist in Canada. Understanding successful CBEP implementation may provide exercise providers with a framework to support
[...] Read more.
Community-based exercise programs (CBEPs) designed for persons with physical disabilities can promote participation in physical activity (PA). Despite their importance, few CBEPs for persons with physical disabilities exist in Canada. Understanding successful CBEP implementation may provide exercise providers with a framework to support the development, implementation, and long-term sustainability of CBEPs. The purpose of this study was to explore CBEP providers’ perceptions of the barriers and facilitators surrounding the initial and ongoing implementation of CBEPs using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research 2.0 (CFIR 2.0). Fifteen eligible CBEPs were identified, of which nine program providers expressed interest in participating in semi-structured interviews. Transcripts were subject to inductive thematic analysis, and codes were deductively mapped onto domains of the CFIR 2.0. Barriers and facilitators were organized into six overarching themes and eighteen subthemes. Across themes, barriers and facilitators were present through initial and ongoing implementation and spanned all five domains of the CFIR 2.0, suggesting factors at all levels influence CBEP implementation. Ultimately, the barriers and facilitators to CBEP implementation may act as a roadmap to support the creation and sustainability of new and existing CBEPs, thereby increasing the number of programs that offer PA opportunities for persons with physical disabilities.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Why We Did It: A Qualitative Analysis of Select Adaptive Gymnastics and Dance Programs
by
Brianna Varner, Matthew Lowery and Martin E. Block
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010020 - 15 Feb 2025
Abstract
For children with disabilities, participation in group physical activities can promote inclusion and a sense of belonging, enhance physical functioning, and improve mental health. Yet, there are very few youth sports programs that offer adaptive programs for children with disabilities. Why do some
[...] Read more.
For children with disabilities, participation in group physical activities can promote inclusion and a sense of belonging, enhance physical functioning, and improve mental health. Yet, there are very few youth sports programs that offer adaptive programs for children with disabilities. Why do some youth sports programs offer these special programs? The purpose of this qualitative study was to understand the experiences and challenges of select youth gymnastics and dance programs in the eastern part of the U.S. that offer adaptive programs for children with disabilities. Nine program directors individually participated in zoom interviews between 45 and 60 min. Results revealed the background of program directors (limited disability experience), why they started their programs (parent requests/personal experiences), challenges faced when creating and sustaining their program (recruitment of participants), advertising the program and recruiting participants (mostly word of mouth), and recruiting and training coaches (within the gym).
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Social Participation Among Adults with Spinal Cord Injury During the Second Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Canada
by
Noémie Fortin-Bédard, Naomie-Jade Ladry, David Bouchard, Caroline Rahn, Jaimie Borisoff, Shane N. Sweet, Kelly P. Arbour-Nicitopoulos, François Routhier and Krista L. Best
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010019 - 12 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic challenged people with spinal cord injury (SCI) regarding a variety of mental and physical issues. New challenges may arise as the effects of the pandemic continue. The objective of this descriptive qualitative study was to explore the social
[...] Read more.
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic challenged people with spinal cord injury (SCI) regarding a variety of mental and physical issues. New challenges may arise as the effects of the pandemic continue. The objective of this descriptive qualitative study was to explore the social participation of Canadians with SCI during the second wave of COVID-19. Methods: Participants with SCI from two Canadian provinces (Quebec and British Columbia) were interviewed. Results: Eighteen participants completed interviews. The facilitators of social participation remain similar since the first wave of COVID-19, such as the use of technology, help received by relatives, and the use of delivery services to obtain groceries and other essentials. Obstacles to mobility due to winter conditions and lack of considerations related to COVID-19 public health measures specific to wheelchair users were also discussed by participants. Conclusions: People with SCI perceived participation restrictions, little changes in life habits, and uncertainty about the future during the second wave of COVID-19. The unique living conditions of people with SCI, ability to adapt life habits, and the lived experiences of people with SCI may have contributed to an overall resilience during the pandemic. Adaptive families, social contacts, and technology made a difference during the pandemic.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Traumatic Brain Injury as an Invisible Disability: Institutional Barriers in Medical, Social and Financial Services in Finland
by
Olivia Emelie Engström, Hisayo Katsui and Lieketseng Ned
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010018 - 6 Feb 2025
Abstract
People who sustain traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) often experience unmet rehabilitation needs. The aim of our research was to explore how the invisible aspects of traumatic brain injury affect the experiences of survivors of TBI in accessing the necessary medical, social, and financial
[...] Read more.
People who sustain traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) often experience unmet rehabilitation needs. The aim of our research was to explore how the invisible aspects of traumatic brain injury affect the experiences of survivors of TBI in accessing the necessary medical, social, and financial assistance. Using Giorgi’s descriptive phenomenological inquiry, we purposefully sampled 11 participants who had experienced TBI when aged 13–27 for interviews. The time since their injuries ranged from 7 to 37 years. Three key themes emerged: (1) lack of knowledge and guidance in medical services, (2) lack of social service assistance, and (3) battles with insurance companies. Our findings show that, due to the hidden nature of TBI-related disabilities and a general lack of societal knowledge about TBI outcomes, survivors face significant difficulties in accessing essential medical, social, and financial services. This study underscores the critical need to address the challenges faced by youth survivors of TBI, as their injuries occur during a pivotal developmental phase when they are developing psychosocial skills, pursuing education, and transitioning into the workforce. Delays or lack of proper medical, social, and financial support hinder rehabilitation and the successful reintegration of these youth into society.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Relationship Between Disability and Children’s Household Chores in Selected Low- and Middle-Income Countries
by
Emma Samman, Lauren Pandolfelli and Claudia Cappa
Disabilities 2025, 5(1), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/disabilities5010017 - 4 Feb 2025
Abstract
Studies on disability and unpaid domestic and care work (UDCW) in low- and middle-income countries are rare. This paper contributes to a nascent body of literature by exploring how children’s unpaid workloads at home are affected by the disability status of their primary
[...] Read more.
Studies on disability and unpaid domestic and care work (UDCW) in low- and middle-income countries are rare. This paper contributes to a nascent body of literature by exploring how children’s unpaid workloads at home are affected by the disability status of their primary caregiver and of younger children within the household in 34 low- and middle-income countries and areas. We constructed ordinary least-squares regression models for the pooled data using country-fixed effects and for each country and area separately. Random effects models are included as a test of robustness. Our analysis of the pooled data revealed that when a household included a child aged 2–4 with a disability, the time dedicated to UDCW by children aged 5–17 rose by approximately 10 percent, on average. While we did not find an association between the disability status of the caregiver and the time children dedicated to UDCW in the pooled regressions, in the country-specific regressions, having a caregiver with a disability was associated with changes in the time spent on UDCW in certain countries, signaling the heterogeneity of country experience. As such, there is reason to devote additional attention to understanding the implications of disability on the amount of time children spend on UDCW and to consider what types of support might be needed in households with diverse disability profiles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Care Economy and Disability Inclusion)
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antioxidants, Biomedicines, Disabilities, JCDD, Hearts
Cardiovascular Disease in Special Populations: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice
Topic Editors: Song-Young Park, Gwenael LayecDeadline: 31 December 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Disabilities
Mental and Physical Health and Well-Being of Individuals with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities
Guest Editor: Janet FinlaysonDeadline: 30 June 2025
Special Issue in
Disabilities
The Care Economy and Disability Inclusion
Guest Editors: Daniel Mont, Monica Pinilla-RoncancioDeadline: 30 June 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Disabilities
Exclusive Papers Collection of Editorial Board Members of Disabilities
Collection Editor: Reinie Cordier






