Journal Description
Foods
Foods
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on food science published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Italian Society of Food Sciences (SISA) and Spanish Nutrition Foundation (FEN) are affiliated with Foods and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, FSTA, AGRIS, PubAg, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Food Science and Technology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Health Professions (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
4.7 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.1 (2023)
Latest Articles
The Functional Components and Hepatic Protective Mechanism of Wolfberry Vinegar by Mixed-Culture Fermentation
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1278; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071278 (registering DOI) - 7 Apr 2025
Abstract
Wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.), as a kind of combination of medicine and food, is rich in antioxidant components. However, the deep-processed products of wolfberry need to be developed to improve its added value. This study aimed to investigate the nutrients, active antioxidant
[...] Read more.
Wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.), as a kind of combination of medicine and food, is rich in antioxidant components. However, the deep-processed products of wolfberry need to be developed to improve its added value. This study aimed to investigate the nutrients, active antioxidant ingredients, and liver-protective mechanism of mixed-culture fermented wolfberry vinegar (MFV). The results showed that MFV had significantly higher protein and significantly lower fat content than wolfberry juice before fermentation, indicating that MFV was a healthy product. The active ingredient content, which included total phenolics, total flavonoids, polysaccharides, betaine, and antioxidant activities, was significantly increased in MFV after mixed-culture fermentation. Moreover, MFV improved histopathological changes and reduced liver biochemical indicators in alcohol-treated mice, indicating the improvement of liver function. In addition, MFV effectively alleviated alcohol-induced liver injury by increasing the expression of alcohol metabolizing enzymes and inhibiting CYP2E1 activity. MFV regulated the equilibrium between pro-oxidant and antioxidant levels by downregulating pro-oxidant markers and upregulating antioxidant markers. Furthermore, MFV reduced the levels of inflammatory indexes by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. These results suggest that MFV is a healthy food for liver protection, which provides a strategy for deep-processed products of wolfberry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Potential Health Benefits of Plant Food-Derived Bioactive Compounds)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Smartphone Video Imaging Combined with Machine Learning: A Cost-Effective Method for Authenticating Whey Protein Supplements
by
Xuan Tang, Wenjiao Du, Weiran Song, Weilun Gu and Xiangzeng Kong
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1277; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071277 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
With the growing interest in health and fitness, whey protein supplements are becoming increasingly popular among fitness enthusiasts and athletes. The surge in demand for whey protein supplements highlights the need for cost-effective methods to characterise product quality throughout the food supply chain.
[...] Read more.
With the growing interest in health and fitness, whey protein supplements are becoming increasingly popular among fitness enthusiasts and athletes. The surge in demand for whey protein supplements highlights the need for cost-effective methods to characterise product quality throughout the food supply chain. This study presents a rapid and low-cost method for authenticating sports whey protein supplements using smartphone video imaging (SVI) combined with machine learning. A gradient of colours ranging from purple to red is displayed on the front screen of a smartphone to illuminate the sample. The colour change on the sample surface is captured in a short video by the front-facing camera. Then, the video is split into frames, decomposed into RGB colour channels, and converted into spectral data. The relationship between video data and sample labels is established using machine learning models. The proposed method is tested on five tasks, including identifying 15 brands of whey protein concentrate (WPC), quantifying fat content and energy levels, detecting three types of adulterants, and quantifying adulterant levels. Moreover, the performance of SVI was compared to that of hyperspectral imaging (HSI), which has an equipment cost of around 80 times that of SVI. The proposed method achieves accuracies of 0.933 and 0.96 in WPC brand identification and adulterant detection, respectively, which are only around 0.05 lower than those of HSI. It obtains coefficients of determination of 0.897, 0.906 and 0.963 for the quantification of fat content, energy levels and milk powder adulteration, respectively. Such results demonstrate that the combination of smartphones and machine learning offers a low-cost and viable preliminary screening tool for verifying the authenticity of whey protein supplements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Anti-Food Fraud: Technologies in Food Safety, Quality and Traceability)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Preparation of Hydrophobic Purple Sweet Potato-Based Intelligent Packaging Films by Stearic Acid Coating and Heat Pressing Treatments
by
Xuanzhuo Liu, Fengfeng Xu, Xiaoqian Huang, Jian Sun, Juan Kan and Jun Liu
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1276; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071276 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
The high hydrophilicity of biopolymer–anthocyanin intelligent packaging films seriously limits their applications in high-humidity environments. Here, a surface hydrophobization technique was adopted to overcome the hydrophilicity of purple sweet potato (PSP)-based intelligent packaging films through stearic acid (SA) coating combined with heat pressing
[...] Read more.
The high hydrophilicity of biopolymer–anthocyanin intelligent packaging films seriously limits their applications in high-humidity environments. Here, a surface hydrophobization technique was adopted to overcome the hydrophilicity of purple sweet potato (PSP)-based intelligent packaging films through stearic acid (SA) coating combined with heat pressing treatments. The structural characteristics, physical properties, and color changeability of the films were investigated. After SA coating treatment, the surface of the films was loosely covered by thick SA layers. As compared with the untreated PSP films, the SA-coated films displayed lower transparency, mechanical property, moisture content, surface wettability, anthocyanin leaching potential, and color changeability. When the SA-coated films were further heat-pressed, the SA-coated layers were closely bound to the films. The heat-pressed films had a higher transparency, mechanical property, and water vapor blocking ability than the SA-coated films. Notably, the color and color changeability of the heat-pressed films were affected by the heat pressing temperature. The films heat-pressed at 100 °C showed a vivid purple color and elevated color changeability, whereas the films heat-pressed at 150 °C showed a brown color and lost color changeability. This study demonstrates that SA coating combined with heat pressing is effective in constructing surface-hydrophobized intelligent packaging films.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Bio-Based Smart Materials for Food Packaging: Applications, Safety, and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Drying Methods on Aroma Profiling of Large-Leaf Green Tea (Camellia sinensis var. Assamica) Determined by HS-SPME-GC-MS
by
Zhengfei Luo, Linlong Ma, Yangtao Zhang, Yanhong Liu, Rui Yang, Xuean Dai, Tiantian Wang, Changmi Lv, Lifeng Zuo, Yanli Liu, Dan Cao, Haibo Yuan, Longfeng Yu and Xiaofang Jin
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1275; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071275 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
Drying methods play a crucial role in the formation of green tea aromas. This study investigated the aroma characteristics and volatile component profiles of large-leaf green tea under hot-air drying, pan-fired drying, and sun drying. The results revealed significant differences in the sensory
[...] Read more.
Drying methods play a crucial role in the formation of green tea aromas. This study investigated the aroma characteristics and volatile component profiles of large-leaf green tea under hot-air drying, pan-fired drying, and sun drying. The results revealed significant differences in the sensory aroma characteristics and volatile components of the large-leaf green tea among the three drying methods. The pan-fire-dried green tea (PDGT) exhibited a distinct roasted aroma, while the hot-air-dried green tea (HDGT) and sun-dried green tea (SDGT) displayed a faint scent and lasting aroma characteristics, with the SDGT additionally featuring a noticeable sun-dried odor. A total of 48 differential volatile components were identified, among which β-Ionone, (E)-β-Ionone, 2,2,6-Trimethylcyclohexanone, Dihydroactinidiolide, BenzeneacetAldehyde, 2-Pentylfuran, 1,1,6-Trimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene, δ-Cadinene, β-Myrcene, Geranylacetone, o-Cymene, 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-one, (E)-β-Ocimene, and BenzAldehyde were identified as the primary contributors to the aroma differences among the three large-leaf green teas. Additionally, 43 differential volatile compounds were found to be significantly correlated with at least one of the aroma types (floral, sweet, green, faint scent, nutty, or roasted). The findings of this study provide a theoretical foundation for understanding the formation of aroma qualities in large-leaf green tea and offer valuable insights for improving its aromatic characteristics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Production, Quality, Flavor Characteristics and Health Benefits of Tea)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Data-Driven Monitoring of Probiotic Fermentation in Fruit Juices Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Aquaphotomics: An Innovative Approach to Food Valorization
by
Lueji Regatieri, Flora Vitalis, Erika Bujna, Quang Duc Nguyen and Zoltan Kovacs
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1274; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071274 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
The nutritional effects of fruit juices, combined with the added value of a probiotic, provide a plant-based fortified functional food. Some process-related drawbacks are caused by the pH parameter, which will affect the survival of probiotics during their industrial processing and storage. By
[...] Read more.
The nutritional effects of fruit juices, combined with the added value of a probiotic, provide a plant-based fortified functional food. Some process-related drawbacks are caused by the pH parameter, which will affect the survival of probiotics during their industrial processing and storage. By means of developing a monitoring method for probiotic activity, the present study aims to investigate the application of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) as a correlative analytical method for fermentation process tracking, in association with the different absorption patterns of bound water, explained by aquaphotomics. The data evaluated in the wavelength range of 1300–1600 nm indicate classification accuracies of 99–100% and 99–93% during calibration and validation, respectively, when applying PCA-LDA for discriminating the fermentation times, for each one of the single and mixed bacterial groups. During PLSR prediction, according to the fermentation times, the validation models developed for pH show coefficients of determination in the range of 0.96 to nearly 1 and root mean square errors of 0.05 and 0.19. On the other hand, for the PLSR prediction of log cell count (CFU/mL), validation modeling shows a coefficient of determination of 0.85 and a root mean square error of 0.23. All things considered, the results support the applicability of combining NIR and aquaphotomics as a bioprocess monitoring tool, which can be further implemented in different studies and industrial contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Discovery and Valorization of New Food Matrices)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Control of Postharvest Soft Rot Caused by Rhizopus stolonifer on Kokei No. 14 Organic Sweet Potato Roots by Carvacrol, Thymol, and Thyme Oil
by
Guangwei Wu, Chenqi Fan, Xueqian Zang, Bei Wang, Yanli Chen, Jingjing Kou and Guopeng Zhu
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1273; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071273 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
Soft rotting caused by Rhizopus stolonifer is one of the most important postharvest decays in Kokei No. 14 organic sweet potato roots. While various methods have been explored for controlling this pathogen, there remains a need for effective, safe, and applicable alternatives, particularly
[...] Read more.
Soft rotting caused by Rhizopus stolonifer is one of the most important postharvest decays in Kokei No. 14 organic sweet potato roots. While various methods have been explored for controlling this pathogen, there remains a need for effective, safe, and applicable alternatives, particularly using essential oils (EOs). This study evaluated the efficacy of EOs, specifically carvacrol, thymol, and thyme oil, in controlling Rhizopus soft rot. We conducted both in vitro and in vivo tests to assess their effects on fungal mycelial growth, spore germination, and the incidence and severity of soft rot in sweet potatoes, along with quality evaluations of the roots. The results indicated that the vapor phase of carvacrol, thymol, and thyme oil was more effective than the contact phase in inhibiting fungal growth and spore germination. In vivo tests revealed that all three EOs significantly reduced the incidence and severity of soft rot, with thymol and thyme oil at 300 mg/L, and carvacrol at 500 mg/L being the most effective. Quality assessments showed minimal impact on properties such as firmness, weight loss, color, starch, carotenoids, and flavonoids, although residual odors increased. GC/MS analysis confirmed that thyme oil contained high levels of both thymol and carvacrol, along with other antimicrobial compounds, suggesting that the cumulative activity of these volatile compounds enhanced their bacteriostatic effects. Thyme oil demonstrated greater efficacy in reducing soft rot development compared to its individual components, making it a promising biofumigant for controlling postharvest diseases in Kokei No. 14 organic sweet potato roots. These findings emphasized the potential for using thyme oil as a safe and effective approach to managing postharvest decay.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Preservatives for Foods)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
(1→3)-α-d-Glucan from the Pink Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus djamor): Structural Features
by
Paulina Adamczyk, Iwona Komaniecka, Marek Siwulski, Kamila Wlizło, Adam Junka, Artur Nowak, Dariusz Kowalczyk, Adam Waśko, Jolanta Lisiecka, Michał Grzymajło and Adrian Wiater
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1272; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071272 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
(1→3)-α-d-Glucan is an important component of the cell wall of most fungi. The polymer has many applications, including as a therapeutic agent in the prevention or treatment of various diseases, as well as a heavy metal sorbent and a component of
[...] Read more.
(1→3)-α-d-Glucan is an important component of the cell wall of most fungi. The polymer has many applications, including as a therapeutic agent in the prevention or treatment of various diseases, as well as a heavy metal sorbent and a component of new materials used in the plastics industry. The presence of (1→3)-α-d-glucan (water-insoluble, alkali-soluble polysaccharide) in the cell wall of Pleurotus djamor (pink oyster mushroom) was confirmed using specific fluorophore-labeled antibodies. Therefore, the water-insoluble fraction (WI-ASF) of P. djamor B123 fruiting bodies was isolated by alkaline extraction and used for further analyses. The structural features of the WI-ASF were determined by composition analysis, linkage analysis, Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectroscopy, 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, as well as viscosity, specific rotation, and gel permeation chromatography. These studies revealed the presence of glucose units linked by α-glycosidic bonds and scanty amounts of mannose and xylose. Furthermore, methylation analysis of WI-ASF demonstrated that the (1→3)-linked glucopyranose (Glcp) is the primary moiety (86.4%) of the polymer, while the 3,4- and 3,6-substituted hexoses are the branching residues of the glucan. The results of chemical and spectroscopic investigations indicated that the analyzed WI-ASF is a (1→3)-linked α-d-glucan type with a molecular weight of 552 kDa.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Edible Fungi: Processing, Storage Preservation, Disease Control, and Potential Bioactivities)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synergistic Amylase and Debranching Enzyme Catalysis to Improve the Stability of Oat Milk
by
Xinyan Zhan, Jinye Zhang, Jiali Xing, Jinyi Xu, Dan Ouyang, Li Wang, Ying Wan and Xiaohu Luo
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1271; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071271 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
Oat starch plays a crucial role in the stability of oat milk. Enzyme-hydrolyzed oat starch has been demonstrated to be an effective means of improving the stability of oat milk. The effects of different enzyme combinations on the stability of oat milk and
[...] Read more.
Oat starch plays a crucial role in the stability of oat milk. Enzyme-hydrolyzed oat starch has been demonstrated to be an effective means of improving the stability of oat milk. The effects of different enzyme combinations on the stability of oat milk and the properties of starch in oats were investigated by adding α-amylase, amyloglucosidase, and different ratios of pullulanase and isoamylase. The results showed that as the degree of hydrolysis increased, the molecular weight, amylose content, and side chain length distribution of the starch decreased significantly. Moreover, compared with oat starch, the rheological and emulsifying properties of the starch hydrolysates were improved, and the characterization of emulsion stability showed that a 1:2 ratio of pullulanase to isoamylase promoted effective debranching and thus improved the stability of oat milk. This study demonstrated that debranching enzymes enhance the enzymatic hydrolysis of beverages and improve the physicochemical properties and stability of oat milk.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Processing of Starch: Structure, Function and Application in Food)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hydroxytyrosol Ameliorates Colon Inflammation: Mechanistic Insights into Anti-Inflammatory Effects, Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Liver Protection
by
Jiali Tang, Mengyao Zhang, Jiaying Wang, Haijing Zhang, Zhong Wang, Ziteng Lei, Chengtao Wang and Wei Chen
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1270; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071270 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic disease influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including genetics, environmental, and gut microbiota. This study aimed to explore the therapeutic potential of the natural polyphenolic compound hydroxytyrosol (HT) in modulating dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis
[...] Read more.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic disease influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including genetics, environmental, and gut microbiota. This study aimed to explore the therapeutic potential of the natural polyphenolic compound hydroxytyrosol (HT) in modulating dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. The findings demonstrate that oral administration of HT significantly alleviated colitis symptoms, as evidenced by a reduction in the disease activity index and improvements in colonic pathology. HT was found to inhibit the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, enhance antioxidant status, and mitigate oxidative stress. Furthermore, HT contributed to the restoration of the gut barrier by reinstating tight junction proteins, reducing the inflammatory marker lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and suppressing inflammation-related genes. This compound also modulated the NLRP3-Cas-1-GSDMD-IL-1β inflammatory pathway and inhibited the NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa B) pathway, thereby alleviating colitis. Gut microbial analysis revealed that HT enriched the abundance of Bacteroidota and altered the balance between Bacteroidota and Firmicutes in mice. Correlation analysis between bacterial microbiota and inflammatory factors suggested that HT may alleviate colitis by modulating the relative abundance of Alistipes, Bacteroides, and unclassified_f__Muribaculaceae. These findings underscore the potential of HT as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of colitis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microbiology, Biochemistry and Potential Human Health Benefits of Fermented Food Products)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
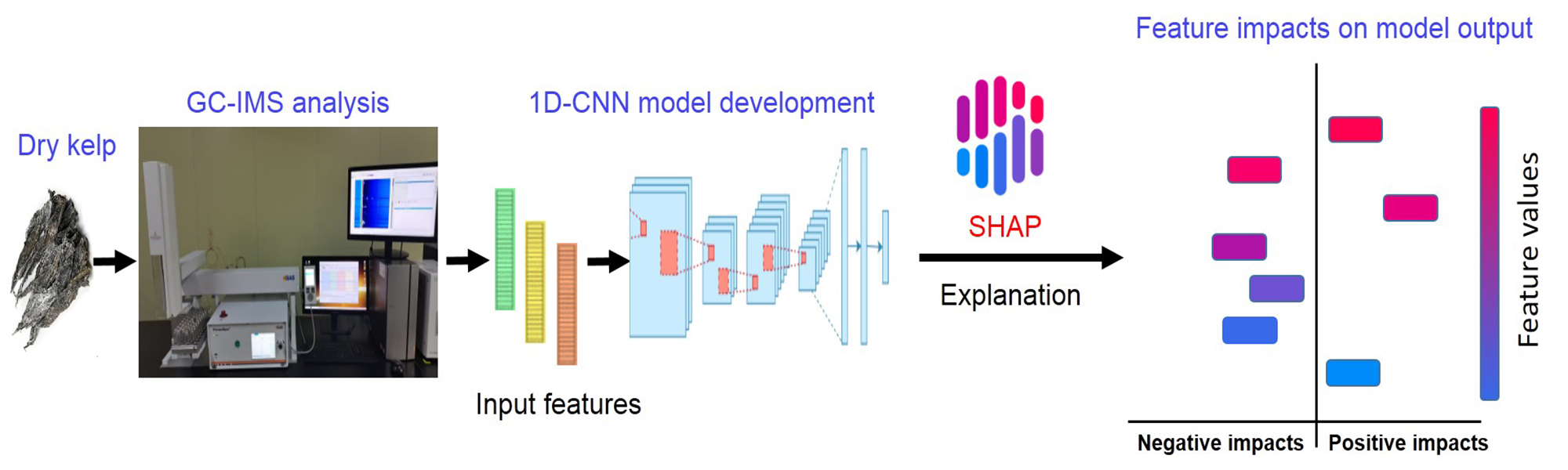
Explainable Deep Learning to Predict Kelp Geographical Origin from Volatile Organic Compound Analysis
by
Xuming Kang, Zhijun Tan, Yanfang Zhao, Lin Yao, Xiaofeng Sheng and Yingying Guo
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1269; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071269 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
In addition to its flavor and nutritional value, the origin of kelp has become a crucial factor influencing consumer choices. Nevertheless, research on kelp’s origin traceability by volatile organic compound (VOC) analysis is lacking, and the application of deep learning in this field
[...] Read more.
In addition to its flavor and nutritional value, the origin of kelp has become a crucial factor influencing consumer choices. Nevertheless, research on kelp’s origin traceability by volatile organic compound (VOC) analysis is lacking, and the application of deep learning in this field remains scarce due to its black-box nature. To address this gap, we attempted to identify the origin of kelp by analyzing its VOCs in conjunction with explainable deep learning. In this work, we identified 115 distinct VOCs in kelp samples using gas chromatography coupled with ion mobility spectroscopy (GC-IMS), of which 68 categories were discernible. Consequently, we developed a comprehensible one-dimensional convolutional neural network (1D-CNN) model that incorporated 107 VOCs exhibiting significant regional disparities (p < 0.05). The model successfully discerns the origin of kelp, achieving perfect metrics across accuracy (100%), precision (100%), recall (100%), F1 score (100%), and AUC (1.0). SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) analysis highlighted the impact of features such as 1-Octen-3-ol-M, (+)-limonene, allyl sulfide-D, 1-hydroxy-2-propanone-D, and (E)-2-hexen-1-al-M on the model output. This research provides deeper insights into how critical product features correlate with specific geographic information, which in turn boosts consumer trust and promotes practical utilization in actual settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Food Fraud as a Global Problem: Advanced Analytical Tools to Detect Species, Country of Origin and Adulterations: Second Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Vineyard Location Impact on the Composition and Quality of Wines from International and Native Varieties Grown in Drama, Greece
by
Adriana Skendi, Aikaterini Karampatea, Elisavet Bouloumpasi, Georgia Tseine, Stefanos Stefanou and Spyridon Mamalis
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1268; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071268 - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
The objective of this work was to investigate the effect of location on the composition and quality of wines from the viticultural zone PGI Drama. Grapes from two white (Sauvignon blanc, Assyrtiko) and three red varieties (Merlot, Cabernet Sauvignon, Agiorgitiko) were collected from
[...] Read more.
The objective of this work was to investigate the effect of location on the composition and quality of wines from the viticultural zone PGI Drama. Grapes from two white (Sauvignon blanc, Assyrtiko) and three red varieties (Merlot, Cabernet Sauvignon, Agiorgitiko) were collected from nine locations within the zone during 2022. The vineyards span distances ranging from several hundred meters to 100 km, and their altitudes vary from 90 to nearly 820 m. Vinification was performed following the same protocol according to the type of wine. Wines were analyzed for quality parameters such as pH, total acidity, alcohol, and residual sugar content. In addition, elemental composition, phenolic content, antioxidant capacity, and sensory attributes of the wines were assessed. The obtained results suggested that besides the type of wine and variety, the location significantly affects the quality parameters of the wine. PCA analysis revealed that location is an important factor affecting the wine quality. The areas north and northwest proved more suitable for specific varieties, as they produce wines with more distinct organoleptic characteristics. The results provide insights into the behavior of international and native varieties in the face of global warming and assist in decisions concerning the most suitable plant material.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Drinks and Liquid Nutrition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advancements and Challenges in Sucralose Determination: A Comparative Review of Chromatographic, Electrochemical, and Spectrophotometric Methods
by
Volodymyr V. Tkach, Tetiana V. Morozova, Isabel O’Neill de Mascarenhas Gaivão, Yana G. Ivanushko, José Inácio Ferrão da Paiva Martins and Ana Novo Barros
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1267; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071267 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
This review presents an in-depth analysis of the latest methods used for the determination of sucralose (E955), focusing on research conducted over the past 10 years. As a widely used sugar substitute in the food and pharmaceutical industries, sucralose has raised concerns about
[...] Read more.
This review presents an in-depth analysis of the latest methods used for the determination of sucralose (E955), focusing on research conducted over the past 10 years. As a widely used sugar substitute in the food and pharmaceutical industries, sucralose has raised concerns about its environmental persistence, potential genotoxicity, and health impacts. This study examines several spectrophotometric, chromatographic, and electrochemical techniques, evaluating their sensitivity, selectivity, and limitations in differentiating sucralose from natural carbohydrates and other sweeteners. The review highlights the pressing need for novel detection methods that not only improve accuracy in trace detection but also address growing concerns about its bioaccumulation and conversion into harmful metabolites. Advancing these analytical techniques is essential for enhancing food safety, public health surveillance, and environmental risk assessment. Chromatographic methods are dominant in sucralose determination in foods and environmental objects, as they allow the determination of sucralose at micro- and nanomolar levels. However, spectrophotometric and electrochemical methods are frequently used as complementary to chromatographic methodologies, sensitizing them. On the other hand, purely spectrophotometric methods are less popular, and electrochemical methods remain underdeveloped. Therefore, the advancement of sucralose determination must be due to cheaper chromatographic and classical electrochemical methods.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Food Chemical Safety)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Listeria monocytogenes and Listeriosis: The Global Enigma
by
Christy E. Manyi-Loh and Ryk Lues
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1266; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071266 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Listeria monocytogenes is an intracellular, Gram-positive, non-spore-forming, non-encapsulated, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, and psychrotrophic food-borne pathogen that causes the infection, listeriosis, thus it attracts great attention following listeriosis outbreaks, which are often associated with high mortality rates. The prevalence of listeriosis is quite low
[...] Read more.
Listeria monocytogenes is an intracellular, Gram-positive, non-spore-forming, non-encapsulated, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, and psychrotrophic food-borne pathogen that causes the infection, listeriosis, thus it attracts great attention following listeriosis outbreaks, which are often associated with high mortality rates. The prevalence of listeriosis is quite low globally; however, the most recent and deadliest outbreak occurred in South Africa, during which 216 persons lost their lives. L. monocytogenes is endowed with the potential to multiply through a wide range of harsh environmental conditions, forming biofilms on varying surfaces in the food industry, as well as having persistent and antibiotic-resistant cells, which pose a major threat and burden to the ready-to-eat food industry. A more frustrating characteristic of this bacterium is its strain divergence, alongside an increased level of antibiotic resistance registered among the strains of L. monocytogenes recovered from food, humans, and environmental sources, especially to those antibiotics involved in the treatment of human listeriosis. Antibiotic resistance exerted by and among pathogenic food-borne microbes is an ongoing public health menace that continues to be an issue. Against this background, a thorough search into different databases using various search engines was performed, which led to the gathering of salient information that was organised, chronologically, based on Listeria monocytogenes and listeriosis. Altogether, the findings elaborated in this study present up-to date knowledge on different aspects of this pathogen which will improve our understanding of the mystery associated with it and the ways to prevent and control its dissemination through ready-to-eat foods. In addition, constant monitoring of the antibiotic resistance profiles of strains of L. monocytogenes from varying sources detected changes, giving an update on the trend in antibiotic resistance. Overall, monitoring of bacterial contamination serves as the key aspect in the control of the food safety output in the food industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Quality and Safety)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional Composition and Flavor Profile of Different Muscle Parts of Hybrid Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai ♀ × H. fulgens ♂)
by
Tongtong Sun, Xiaoting Chen, Zhiyu Liu, Chenyang Xie, Shuji Liu, Yongchang Su, Nan Pan, Kun Qiao and Wenzheng Shi
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1265; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071265 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
This study analyzed the basic nutritional components and amino acid, fatty acid, and mineral composition of hybrid abalone Haliotis discus hannai ♀ × H. fulgens ♂ adductor (AM), transition (TM), and skirt (SM) muscles. The taste characteristics of the muscles were measured via
[...] Read more.
This study analyzed the basic nutritional components and amino acid, fatty acid, and mineral composition of hybrid abalone Haliotis discus hannai ♀ × H. fulgens ♂ adductor (AM), transition (TM), and skirt (SM) muscles. The taste characteristics of the muscles were measured via electronic tongue, and the volatile compounds were identified by headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS) analysis. Compared to SM, AM and TM exhibited relatively similar basic nutritional compositions. Although SM exhibited the highest moisture content (84.67%), its protein content (only 11.83%) and total carbohydrate content (only 0.19%) were significantly lower than those of AM (20.42% and 4.14%) and TM (19.10% and 4.48%). The ash and fat contents were similar across the three muscle parts. The amino acid composition was consistent across three parts, and AM showed the highest total amino acid content, ratio of essential amino acids, and essential amino acid index. All three muscle parts were rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, but the content was higher in AM and TM than in SM. The mineral elements were rich in variety, with high K, P, Mg, and Zn contents. Bitterness intensities were lower and umami and richness intensities were higher in AM and TM than in SM. The contents of volatile compounds related to fishy odor were higher in TM and SM than in AM. The results provided a scientific basis for the intensive processing and comprehensive utilization of Haliotis discus hannai ♀ × H. fulgens ♂.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Aquatic Products Processing and Preservation Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Possible Genotoxic Effects of Post-Harvest Fungicides Applied on Citrus Peels: Imazalil, Pyrimethanil, Thiabendazole and Their Mixtures
by
Boglárka Bernadett Tisza, Luca Járomi, Judit Háhn, Bálint Bérczi, Andrea Horváth-Sarródi, Andrea Gubicskóné Kisbenedek and Gellért Gerencsér
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1264; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071264 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Post-harvest fungicides are frequently used on citrus peels to reduce post-harvest fungal contamination during the storage and transport of products. Despite these positive effects, fungicides can pose health risks to consumers. The aim of our study was to perform a genotoxicological risk assessment
[...] Read more.
Post-harvest fungicides are frequently used on citrus peels to reduce post-harvest fungal contamination during the storage and transport of products. Despite these positive effects, fungicides can pose health risks to consumers. The aim of our study was to perform a genotoxicological risk assessment of imazalil, pyrimethanil, thiabendazole and their mixtures used as post-harvest treatments. A Salmonella mutagenicity Ames test and comet assay were performed to detect reverse mutation and assess DNA damage. Base-pair, frameshift mutations and metabolic activity were analyzed using the Ames test. In the comet assay, lymphocytes were treated with fungicides for 4 and 24 h. Thiabendazole was found to induce both frameshift and base-pair mutations in the Ames test despite the mutagenicity of both imzalil and pyrimethanil (p < 0.05). DNA-strand breaks were observed in lymphocytes, mainly with dimethyl-sulfoxide solvent fungicides (p < 0.05). The long-term exposure and consumption of fruits and vegetables treated with fungicides can increase the risks of developing genotoxic tumors. Our findings raise new questions about the health risks of fungicides and their mixtures to consumers. Further investigations are essential to explore the genotoxicological effects of fungicides on citrus peels.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Risk Assessment of Hazardous Pollutants in Foods)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Glycosidase Production by Rhodotorula mucilaginosa on the Release of Flavor Compounds in Fermented White Radish
by
Huixin Zhang, Rui Wang, Yaoying Wang, Yanfei Wang, Tao Wang, Chuanqi Chu, Shengbao Cai, Junjie Yi and Zhijia Liu
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1263; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071263 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Fermented vegetables are highly valued by consumers for their distinct flavors and rich nutritional content. Microbial fermentation imparts distinct flavors to these vegetables, with red yeast being a common microorganism involved in the fermentation process. However, studies on the impact of red yeast
[...] Read more.
Fermented vegetables are highly valued by consumers for their distinct flavors and rich nutritional content. Microbial fermentation imparts distinct flavors to these vegetables, with red yeast being a common microorganism involved in the fermentation process. However, studies on the impact of red yeast on flavor development in fermented vegetables remain scarce. This study employed multi-omics to analyze the effect of glycosidase produced by Rhodotorula mucilaginosa on the release of bound flavor compounds in vegetables. The results indicate that the yeast possesses multiple glycosidase-encoding genes, with the activities of α-galactosidase, β-glucosidase, and α-mannosidase being detected. Following the inoculation of yeast into fermented vegetable juice, a significant increase was observed in the expression of the β-glucosidase gene (bglX) and the α-glucosidase maltase gene (malL), alongside an increase in the content of flavor compounds correlated with the enzymatic activity detected. The application of commercial glycosidase to vegetable juice resulted in increased levels of cis-2-pentenol, hyacinthin, geranylacetone, and 1-dodecanol, consistent with findings from yeast-fermented vegetable juice. Thus, Rhodotorula mucilaginosa can secrete glycosidases that hydrolyze and release endogenous bound flavor compounds in vegetables, thereby enhancing the flavor quality of the final product.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Biotechnology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Low Temperature and Nitrogen Modified Atmosphere Treatments on the Storage of High Moisture Indica Rice: Quality, Microstructure, and Metabolome Characteristics
by
Yanan Zhao, Lulu Li, Yanfei Li and Yan Zhao
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1262; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071262 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Effects of low temperature (LT, 20 °C) combined with nitrogen-modified atmosphere (MA, 95% N2) storage (LT + MA) on quality, microstructure, and metabolome characteristics of high moisture content (15.5%) during 180 days of storage were investigated to explore a potential preservation
[...] Read more.
Effects of low temperature (LT, 20 °C) combined with nitrogen-modified atmosphere (MA, 95% N2) storage (LT + MA) on quality, microstructure, and metabolome characteristics of high moisture content (15.5%) during 180 days of storage were investigated to explore a potential preservation technique for high moisture rice. The results showed that after 180 days of storage, the fatty acid value, malondialdehyde content, and amylose content of rice under LT + MA storage were 53.33%, 72.93%, and 91.85% of those under conventional storage (CS, conventional atmosphere, 30 °C, RH 65%), respectively. The color, pasting properties, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of the LT + MA treatment were found to be markedly superior to those of the CS treatment. In addition, the differential metabolites sucrose, trehalose-6P, trehalose, 3,7-Di-O-methylquercetin (DMQ), rutin, and vitexin 2″-O-rhamnoside (VOR) were screened to assess for sensitivity to changes in storage conditions. The study demonstrated that the LT + MA effectively suppressed the escalation of FAV, MDA content, and amylose content. In addition, it was observed to inhibit the deterioration of color and pasting properties while concurrently maintaining the polygonal shape of rice starch granules. Furthermore, the differential metabolites of non-targeted metabolomics indicated that the LT + MA group exhibited superior efficacy in retarding rice aging.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations in Grain Storage and Processing: Strategies for Reducing Losses and Enhancing Food Product Quality)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Glutinous Rice Varieties from Different Regions on Microbial Community Structure, Metabolic Profiles, and Flavor Characteristics of Chinese Rice Wine (Huangjiu)
by
Qi Peng, Linyuan Li and Guangfa Xie
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1261; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071261 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Huangjiu is a traditional alcoholic beverage in China, but because of the differences in fermentation conditions and raw materials, how to optimize the flavor quality of Huangjiu is facing challenges. This study used high-throughput sequencing (HTS) to investigate microbial diversity in Huangjiu brewed
[...] Read more.
Huangjiu is a traditional alcoholic beverage in China, but because of the differences in fermentation conditions and raw materials, how to optimize the flavor quality of Huangjiu is facing challenges. This study used high-throughput sequencing (HTS) to investigate microbial diversity in Huangjiu brewed from glutinous rice from five regions in China. Metabolic pathway annotation, electronic senses, and metabolite analysis elucidated the relationships between rice variety, microbial communities, flavor profiles, and metabolic characteristics of Huangjiu. Statistically significant differences in microbial community structure and flavor profiles were observed across Huangjiu samples (p < 0.05), with ten dominant microbial genera identified. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) enriched in Guizhou and Hubei were positively correlated with higher organic acid (12.36 and 12.30 mg/mL, respectively) and lower amino acid levels (2985 and 2920 mg/L, respectively), contributing to a more pronounced sourness in these Huangjiu. Conversely, Huangjiu from Zhejiang, Guangxi, and Jilin exhibited higher concentrations of Saccharopolyspora, Saccharomonospora, Saccharomyces, and Bacillus, associated with elevated amino acid (3706, 3695, and 3700 mg/L, respectively) and reduced organic acid levels (10.11, 9.92 and 10.10 mg/mL, respectively), resulting in sweetness and bitterness. These findings provide valuable insights for optimizing Huangjiu flavor and quality through targeted microbial and fermentation management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Grain)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mechanism Analysis of Amphotericin B Controlling Postharvest Gray Mold in Table Grapes
by
Yingying Wu, Jingyi Wang, Shenli Wang, Yijie Ke, Tianyi Ren and Ying Wang
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1260; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071260 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Gray mold, caused by Botrytis cinerea, is the primary factor contributing to postharvest losses in table grape fruit. In this study, we have identified amphotericin B (AMB), a natural compound originating from Streptomyces nodosus, as a promising agent in managing postharvest
[...] Read more.
Gray mold, caused by Botrytis cinerea, is the primary factor contributing to postharvest losses in table grape fruit. In this study, we have identified amphotericin B (AMB), a natural compound originating from Streptomyces nodosus, as a promising agent in managing postharvest gray mold in table grapes. In vitro experiments demonstrated that 0.2 mg/L AMB achieved an inhibition rate of over 90% against B. cinerea in PDA medium, and in vivo assays on grape berries showed that 200 mg/L AMB treatment could completely suppress the occurrence of gray mold disease. A mechanism analysis found that AMB treatment disrupted the plasma membrane structure, which consequently triggered cellular leakage and induced cell death. Furthermore, AMB application effectively modulated the transcriptional profile of genes related to redox homeostasis, transmembrane transport, and peroxidase functions in B. cinerea, thereby reducing the virulence of the fungus. In addition, AMB treatment had the potential to activate defense mechanisms in table grapes by enhancing the activities of ROS-scavenging enzymes and defense-associated enzymes. Collectively, AMB can be regarded as a natural antifungal agent that effectively combats B. cinerea, thereby extending the postharvest shelf life of table grape fruit.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations in Postharvest Physiology and Technology: Key to Optimizing the Quality of Fruits and Vegetables)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Changes in Quality and Metabolites of Pickled Purple Radish During Storage
by
Seung-Hun Chae, Sang-Hyeon Lee, Seung-Hwan Kim, Si-Hun Song, Jae-Hak Moon, Heon-Woong Kim and Jeong-Yong Cho
Foods 2025, 14(7), 1259; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071259 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
This study investigated the changes in the physicochemical properties and metabolites of pickled purple radish during storage. Pickles of purple radish (‘Boraking’) prepared by the addition of acetic acid and sugar were stored in the dark at 4 °C for 60 days. The
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the changes in the physicochemical properties and metabolites of pickled purple radish during storage. Pickles of purple radish (‘Boraking’) prepared by the addition of acetic acid and sugar were stored in the dark at 4 °C for 60 days. The color of the pickled purple radish changed from purple to pink, while the pickling solution changed from pink to purple. During storage, sucrose content gradually decreased, while glucose and fructose levels increased. LC-ESI-QToF-MS metabolomic analysis indicated that metabolites, including organic acids, amino acids, sulfur-containing compounds, lysophosphatidylcholine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, and anthocyanins, were identified. The antioxidant capacity and color meter of pickled purple radish may undergo changes due to the altered levels of non-volatile compounds (cyanidins, adenosine, and amino acids) during storage. Anthocyanins had negative correlations with the color of pickled purple radish. The radical scavenging activity and ferric-reducing antioxidant power of pickled purple radish declined during storage. These findings emphasized the need for further research to develop processing and storage methods that enhance the bioactivity and stability of pickled purple radish.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Development of New Functional Foods and Ingredients: 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Foods Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Analytica, Foods, Molecules, Processes, Separations
New Trends on Separation and Extraction of Bioactive Compounds and Respective Applications
Topic Editors: Isabel Maria Duque Martins, Madalena M. DiasDeadline: 30 April 2025
Topic in
CIMB, Foods, IJMS, Sci. Pharm., Antioxidants, Nutrients
Nutrients, Food Bioactives, and Functional Foods in Gastrointestinal and Metabolic Disorders
Topic Editors: Samuel Fernández-Tomé, Ortega Moreno LorenaDeadline: 31 May 2025
Topic in
Chemistry, Foods, IJMS, Molecules, Separations
Recent Trends and Advances in Food Authentication and Traceability
Topic Editors: Michael Kontominas, Anastasia BadekaDeadline: 30 June 2025
Topic in
Biomolecules, Energies, Foods, IJMS, Polymers
Microbes and Their Products for Sustainable Human Life
Topic Editors: Shashi Kant Bhatia, Ranjit GuravDeadline: 7 July 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Foods
Bioactivities of Natural Products Extracted from Plant Foods and Their Application in Food Industries
Guest Editors: Xin Yang, Lizhi Liu, Caili FuDeadline: 9 April 2025
Special Issue in
Foods
Probiotics in the Dairy Product: Trends, Advances and Opportunities
Guest Editors: Carlos Dias Pereira, Marta H. HenriquesDeadline: 10 April 2025
Special Issue in
Foods
Recent Advances in Cheese and Fermented Milk Production, 2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Katarina Lisak Jakopović, Irena Barukcic, Rajka BožanićDeadline: 10 April 2025
Special Issue in
Foods
Utilization of Plant Protein for Functional Food Ingredients and Biobased Products
Guest Editors: Shuying Li, Miao HuDeadline: 10 April 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Foods
Edible Films and Coatings for Food Preservation
Collection Editor: Hiléia Karla Silva Souza
Topical Collection in
Foods
Milk and Dairy Products: Chemistry, Structure, Processing and Properties
Collection Editor: Débora Parra Baptista
Topical Collection in
Foods
Phytonutrients in Food: From Traditional to Rational Usage
Collection Editor: Quanhong Li








