-
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Bacterial Platform for Biopharmaceutical Production
Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Bacterial Platform for Biopharmaceutical Production -
 Biological Evaluation of 3-Aryl and/or 4-(N-Aryl)aminocoumarins Against Human Pathogens: Antileishmanial and Antiviral Activities
Biological Evaluation of 3-Aryl and/or 4-(N-Aryl)aminocoumarins Against Human Pathogens: Antileishmanial and Antiviral Activities -
 The Use of Personalized Medicine in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC): New Therapeutic Opportunities
The Use of Personalized Medicine in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC): New Therapeutic Opportunities
Journal Description
Future Pharmacology
Future Pharmacology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on pharmacology, drug discovery, and therapeutics published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Future Pharmacology is a companion journal of Pharmaceutics.
Latest Articles
Antioxidant Activity and Anxiolytic Effect of Cnidoscolus quercifolius Pohl Stem Bark Extract in Zebrafish
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5020016 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Cnidoscolus quercifolius, popularly known as “favela”, is used in traditional medicine to treat various conditions, such as infections and inflammations. However, its therapeutic potentials remain underexplored in scientific research. The present study aimed to evaluate the anxiolytic effect, toxicity, and antioxidant
[...] Read more.
Background: Cnidoscolus quercifolius, popularly known as “favela”, is used in traditional medicine to treat various conditions, such as infections and inflammations. However, its therapeutic potentials remain underexplored in scientific research. The present study aimed to evaluate the anxiolytic effect, toxicity, and antioxidant activity of methanolic (EMCq) and ethyl acetate (EAECq) extracts of C. quercifolius bark, as well as determine their chemical composition by HPLC/DAD and their levels of phenolic compounds and flavonoids. Methods: Anxiolytic effect and acute toxicity tests were conducted using the zebrafish model, while antioxidant activity was assessed using the DPPH• and ABTS+ methods. The chemical composition was obtained by HPLC/DAD, and phenolic compounds and flavonoids were quantified with the Folin–Ciocalteu reagents and the aluminum chloride colorimetric method, respectively. Results: Caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, cinnamic acid, pinocembrin, and apigenin were identified and quantified. The results indicated that both extracts exhibited low antioxidant activity, possibly due to their low levels of phenols (0.187 and 0.293 mg GAE/g) and flavonoids (0.84 and 0.64 mg QE/g). However, the extracts did not show acute toxicity (>400 mg/kg) and reduced the locomotor activity of zebrafish at all the doses tested (40 to 400 mg/kg), while increasing the time the animals remained in the light zone, indicating an anxiolytic effect. Conclusions: These findings suggest for the first time that C. quercifolius has anxiolytic properties, warranting further investigation into specific bioactive compounds and their mechanisms of action. Future studies may explore molecular analysis techniques to identify the responsible compounds, as well as investigate safety and clinical efficacy in mammalian models.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Synergistic Antinociceptive Effects of Ketorolac and Ascorbic Acid in a Formalin-Induced Pain Model
by
Josué Vidal Espinosa-Juárez, Erika Florecita Hoover-Lazo, Sergio de Jesús Rubio-Trujillo, Citlaly Natali de la Torre-Sosa, Nereida Violeta Vega-Cabrera, Josselin Carolina Corzo-Gómez, Refugio Cruz-Trujillo and Osmar Antonio Jaramillo-Morales
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5020015 - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
Pain is a widespread global issue and one of the most common disabling conditions in daily life. A wide range of medications are available to reduce or eliminate pain, with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) being among those most commonly used. Additionally, new analgesic
[...] Read more.
Pain is a widespread global issue and one of the most common disabling conditions in daily life. A wide range of medications are available to reduce or eliminate pain, with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) being among those most commonly used. Additionally, new analgesic approaches, such as antioxidants (Ascorbic Acid), have been explored for their potential to relieve acute pain after surgery, cancer-related pain, and chronic pain not related to cancer with fewer adverse effects. Furthermore, the use of pharmacological combinations is an alternative treatment strategy to obtain a higher efficacy using lower drug concentrations, at which side effects are minimal. Background/Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate the pharmacological synergism of ketorolac and ascorbic acid in an inflammatory pain model. Methods: The individual and combined effects of ketorolac and ascorbic acid were evaluated in a formalin-induced pain model in mice. Four experimental groups were established: control (vehicle), ketorolac (KET), ascorbic acid (AA), and combination (KET/AA). Results: The combination of ketorolac and ascorbic acid produced a greater antinociceptive effect compared to the vehicle and individual treatments in the formalin model. Notably, even the lowest dose of the combination (KET 6.26/AA 3.21 µg/paw) exhibited a stronger effect than the maximum doses of each individual treatment KET (100 µg/paw) and AA (100 µg/paw). The effective concentration that produced 30% of antinociception (EC30) for the tested treatments were determined, and an isobologram analysis confirmed the presence of a synergistic interaction in these combinations. Conclusions: These findings suggest that the combination of ketorolac and ascorbic acid produces a synergistic antinociceptive effect in the formalin-induced pain model. The enhanced efficacy of the combination indicates a potential therapeutic advantage in pain management by reducing the required dosage of each compound while maintaining or improving analgesic effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Therapeutic Approach to Inflammation and Pain)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Trifluralin Toxicology Revisited: Microtubule Inhibition, Mitochondrial Damage, and Anti-Protozoan Potential
by
Darío Lirussi
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5020014 - 23 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The aim of this review is to evaluate the therapeutic possibilities of trifluralin and other 2,6-dinitroaniline herbicides by assessing different aspects of trifluralin’s toxicology (including its mitochondrial toxicity), pharmacokinetics, and environmental fate. The particular features of TFL have triggered a wide range of
[...] Read more.
The aim of this review is to evaluate the therapeutic possibilities of trifluralin and other 2,6-dinitroaniline herbicides by assessing different aspects of trifluralin’s toxicology (including its mitochondrial toxicity), pharmacokinetics, and environmental fate. The particular features of TFL have triggered a wide range of policies about its properties. Is has been banned in some countries and, at the same time, has been proposed as a drug for the cure of parasitic disease by some scientific research articles. The use of this pre-emergence herbicide to control broadleaf weeds and annual grasses is assumed to rely only on its microtubule depolarization or cytoskeleton disassembly abilities (on-target effect), a fact that justifies its inhibition of a wide range of microorganisms (mostly protozoans), sharing a relatively high degree of conservation in tubulin protein sequences with weeds and grasses. Recent studies have confirmed that TFL also affects mitochondrial function (off-target effect), a hypothesis previously suggested in earlier works. Here, we account for the main issues in TFL toxicology, other potential uses of the herbicide outside crops, and its feasibility for use as an antiprotozoal drug.
Full article
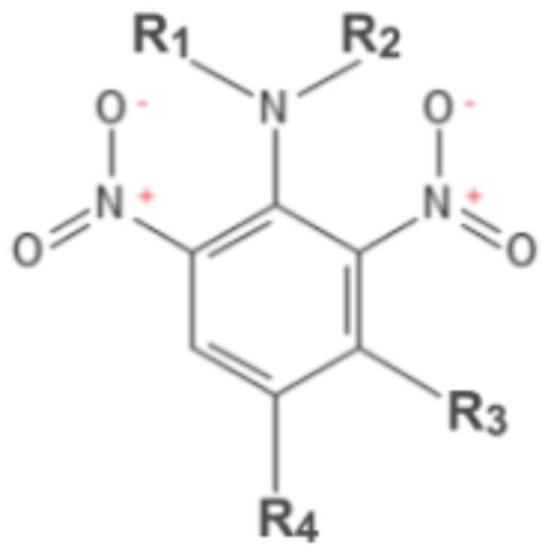
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Interaction of Microcolin Cyanobacterial Lipopeptides with Phosphatidylinositol Transfer Protein (PITP)—Molecular Docking Analysis
by
Christian Bailly and Gérard Vergoten
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010013 - 17 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Microcolins A–M are cytotoxic marine lipopeptides produced by the cyanobacterium Moorena producens, also known as Lyngbya majuscula. Recent studies have shown that two compounds in the series, microcolins B and H, can form covalent complexes with phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins α and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Microcolins A–M are cytotoxic marine lipopeptides produced by the cyanobacterium Moorena producens, also known as Lyngbya majuscula. Recent studies have shown that two compounds in the series, microcolins B and H, can form covalent complexes with phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins α and β (PITPα/β) upon the reaction of their α,β-unsaturated ketone group with the thiol group of a key cysteine residue of PITP. These observations prompted us to compare the binding of all microcolins and a few related derivatives (VT01454 and (deoxy)majusculamide D) to PITP to delineate structure–binding relationships. Methods: A molecular docking analysis led to the identification of microcolin E as the potentially best PITPα binder in the series, followed by microcolins B and H and analog VT01454. The computational data agree well with the published experimental results. Results: The binding of microcolin H into a large cavity of PITPα positions its reactive electrophilic α,β-unsaturated ketone close to the thiol of Cys95, enabling the facile formation of a covalent C-S linkage. A similar bonding can occur with the Cys94 of PITPβ. Molecular models of microcolins bound to PITP were compared to identify structural elements chiefly implicated in the recognition process. Conclusions: This computational study provides guidance in the design of microcolin derivatives targeting PITPα/β considered targets for cancer and inflammatory pathologies.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Sinensetin, Eupatilin, and Jaceosidin on Human Melanogenesis: A Pilot Study
by
Shilpi Goenka
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010012 - 14 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Flavones, a class of plant-based flavonoids, have demonstrated conflicting anti-melanogenic activities in mouse and human melanocytes. Sinensetin (SNT), a polymethoxyflavone, has shown pro-melanogenic activity in B16F10 mouse melanoma (MM) cells, while eupatilin (EU) and jaceosidin (JAC), two flavones that are structural analogs
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Flavones, a class of plant-based flavonoids, have demonstrated conflicting anti-melanogenic activities in mouse and human melanocytes. Sinensetin (SNT), a polymethoxyflavone, has shown pro-melanogenic activity in B16F10 mouse melanoma (MM) cells, while eupatilin (EU) and jaceosidin (JAC), two flavones that are structural analogs of SNT, have not been evaluated for their effects on melanogenesis yet. Methods: Herein, the effects of SNT, EU, and JAC on melanogenesis in MNT-1 cells (human melanoma) and HEMn-DP cells (primary human melanocytes) have been examined. The mushroom tyrosinase (TYR) activity was tested in cell-free conditions, followed by examination of the cytotoxicity of the compounds via the Alamar Blue (AB) assay. Cellular melanin production and TYR activity were estimated in MNT-1 cells. The compounds were further examined in primary human melanocytes for melanin production, TYR activity, and protein levels. Results: Our findings show that SNT was a potent inhibitor of TYR activity in a cell-free assay, while EU and JAC had no effect. However, both SNT and EU were shown to exhibit anti-melanogenic activity (that was reversible) in human cells, while JAC was ineffective and cytotoxic. Conclusions: SNT and EU are potential novel candidates for hyperpigmentation treatment without cytotoxicity. Additional studies are warranted to elucidate the signaling mechanisms that govern their anti-melanogenesis action. Future research is necessary to assess the anti-melanogenic effectiveness of SNT/EU using 3D skin tissue equivalents and to select the optimal candidate.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
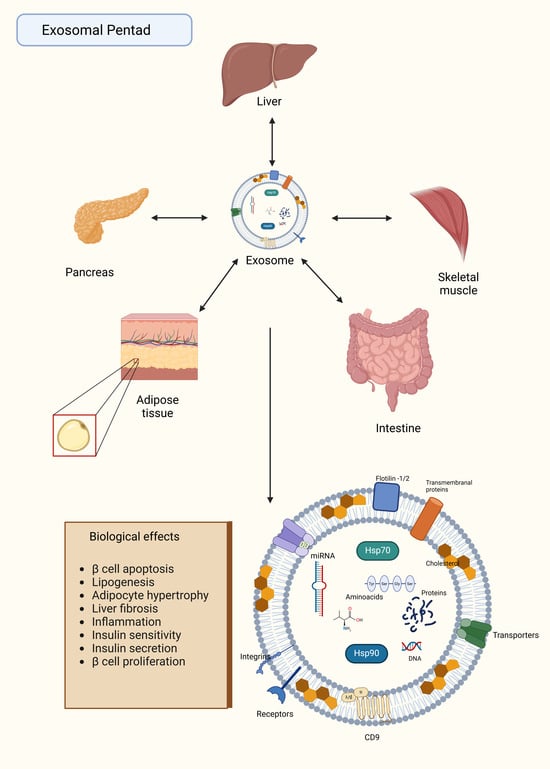
Inter-Tissue Communication Mechanisms via Exosomes and Their Implications in Metabolic Diseases: Opportunities for Pharmacological Regulation
by
Brenda Chimal-Vega, Jesus Emanuel Maldonado-Arvizu, Alex Daniel Hernández Avalos, José Fernando Díaz-Villanueva, Luis Pablo Avila-Barrientos and Victor G. García González
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010011 - 6 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Exosomes can transport regulatory biomolecules and are mediators of cellular signaling among metabolic tissues through endocrine mechanisms. Understanding the pathways and processes underlying exosome-mediated inter-tissue communication is critical for elucidating the molecular pathophysiology of metabolic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus
[...] Read more.
Exosomes can transport regulatory biomolecules and are mediators of cellular signaling among metabolic tissues through endocrine mechanisms. Understanding the pathways and processes underlying exosome-mediated inter-tissue communication is critical for elucidating the molecular pathophysiology of metabolic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and cardiovascular disorders. Consequently, these mechanisms represent novel and promising targets for pharmacological regulation. We examined the current knowledge regarding exosome physiology, the mechanisms of interaction with target tissues, and its role in metabolic tissue communication. We also analyzed the secretory profiles of exosomes in metabolic tissues, emphasizing their regulatory roles in adipose tissue, liver, pancreas, skeletal muscle, and the small intestine, while discussing their association with metabolic diseases. In this sense, we propose the exosomal pentad as a novel framework highlighting exosome-mediated inter-organ communication, where exosomes may regulate a metabolic axis involving these tissues. This model aligns with the ominous octet in type 2 diabetes but emphasizes exosomes as key regulators of metabolic homeostasis and potential therapeutic targets. The role of exosomes for the treatment of metabolic diseases emerges as a critical area of pharmacologic exploration. For instance, therapeutic strategies that prevent target tissue binding or expression of cargo molecules such as miRNAs could be designed, using antagomiRs or nanoparticles. Additionally, integrins like αvβ5 on the exosomal membrane can be blocked with monoclonal antibodies or engineered for targeted delivery of therapeutic molecules. Exosomes, critical mediators of inter-organ communication and metabolic regulation, hold potential to design precise molecular-level therapies while minimizing systemic side effects.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Water-Soluble Cu(II) Complexes with Polypyridyl Ligands: Anticancer Activity and DNA Interaction
by
Herisson F. dos Santos, Nádija N. P. da Silva, George B. S. Pereira, Mauro A. Lima, Nailton M. Nascimento-Júnior, Renan L. de Farias, Amos O. Akinyemi and Fillipe V. Rocha
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010010 - 19 Feb 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Cu(II) complexes with polypyridine ligands have shown carcinogenic activity already described in the literature and appear as a possible alternative to cisplatin, which has several side effects. In view of this, four Cu(II) complexes with the formulas [Cu(L1)(H2O)2](PF
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Cu(II) complexes with polypyridine ligands have shown carcinogenic activity already described in the literature and appear as a possible alternative to cisplatin, which has several side effects. In view of this, four Cu(II) complexes with the formulas [Cu(L1)(H2O)2](PF6)2 (A1) and [Cu(L2)(H2O)2](PF6)2 (A2), [Cu(L1)(bipy)](PF6)2 (B1) and [Cu(L2)(bipy)](PF6)2 (B2) were synthesized, where L1 = dipyrido[1,2,5]oxadiazolo[3,4-b]quinoxaline, L2 = 6,7-dicyanodipyrido[2,2-d:2,3-f]quinoxaline, and bipy = 2,2′-bipyridine. Methods: The proposed structures supported characterization techniques (molar conductivity, elemental analyses, absorption spectroscopy in the infrared region, and UV–vis). The interaction of the complexes with DNA was evaluated through an ethidium bromide displacement assay, complemented by theoretical studies using molecular docking. Additionally, the cytotoxic activity of the complexes was tested against DU 145 (prostate tumor), MCF-7 (breast tumor), and PNT-2 (non-tumor prostate) cell lines, with all complexes showing promising results. Results: Among them, complex B1 exhibited the highest number of DNA contacts in molecular docking studies, a binding constant of 3.7 × 106 in the ethidium bromide displacement assay. It was the most selective complex (IS = 5.43) for the DU 145 (prostate tumor) cell line, demonstrating greater selectivity than cisplatin. Conclusions: This study has demonstrated the potential of the Cu(II) complexes obtained, which could be an alternative to platinum complexes in the future
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Discovery of Arylfuran and Carbohydrate Derivatives from the BraCoLi Library as Potential Zika Virus NS3pro Inhibitors
by
Fernanda Kelly Marcelino e Oliveira, Beatriz Murta Rezende Moraes Ribeiro, Ellen Gonçalves de Oliveira, Marina Mol Sena Andrade Verzola, Thales Kronenberger, Vinícius Gonçalves Maltarollo, Ricardo José Alves, Renata Barbosa de Oliveira, Rafaela Salgado Ferreira, Jônatas Santos Abrahão and Mateus Sá Magalhães Serafim
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010009 - 15 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Zika fever is a disease caused by the Zika virus (ZIKV). Symptomatic cases may be associated with neurological disorders in adults, as well as congenital Zika syndrome and other birth defects during pregnancy. In 2016, Zika fever was considered a public health
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Zika fever is a disease caused by the Zika virus (ZIKV). Symptomatic cases may be associated with neurological disorders in adults, as well as congenital Zika syndrome and other birth defects during pregnancy. In 2016, Zika fever was considered a public health problem by the World Health Organization (WHO), highlighting the need to develop new therapies against the disease. Currently, there is no antiviral or vaccine available to treat or prevent severe cases. Due to the lack of available therapeutics and few promising hit molecules, we computationally screened the well-described ZIKV protease (NS3pro) as a drug target to revisit the small-molecule database Brazilian Compound Library (BraCoLi) and select potential inhibitors. Methods: We employed a consensus docking screening of a library of 1176 compounds using GOLD and DockThor. We selected 28 hits based on predicted binding affinity, and only the remnants of three compounds were available in the library at the time of this study for experimental validation. The hits were evaluated for their cytotoxic (CC50) and effective concentrations (EC50) for their potential antiviral activity in Vero cells. Results: The three hit compounds presented modest CC50 values of 89.15 ± 3.72, >100, and 29.67 ± 1.01 μM, with the latter, a carbohydrate derivative, having an EC50 value of >12.5 μM (~40% inhibition) against ZIKV PE243. Additionally, the essentially non-toxic compound, an arylfuran derivative, also inhibited the ZIKV NS3pro with an IC50 value of 17 μM but presented evidence of acting through a promiscuous mechanism for enzyme inhibition. Conclusion: This study highlights the relevance of revisiting existing small-molecule assets to identify novel therapeutic starting points against ZIKV, aiming for potential lead candidates in the future.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCommunication
The Effect of Agave Bagasse Extract on Wound Healing in a Murine Model
by
Herminia López-Salazar, Elizabeth Negrete-León, Brenda Hildeliza Camacho-Díaz, Juan José Acevedo-Fernández, Sandra Victoria Ávila-Reyes and Martha L. Arenas Ocampo
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010008 - 5 Feb 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The development of bioproducts that can accelerate wound healing is a key focus in biomedicine, especially when these products are derived from sustainable by-products. This study investigates the wound-healing potential of an extract obtained from Agave angustifolia Haw bagasse (BagEE) using microwave
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The development of bioproducts that can accelerate wound healing is a key focus in biomedicine, especially when these products are derived from sustainable by-products. This study investigates the wound-healing potential of an extract obtained from Agave angustifolia Haw bagasse (BagEE) using microwave extraction.Methods: HPLC-MS analysis was performed to identify the main compounds present in BagEE, revealing quercetin, isorhamnetin, diosgenin, hecogenin, manogenin, β-sitosterol glucoside, and β-sitosterol as tentative constituents. A murine excision wound model was employed to assess the efficacy of BagEE. The experimental group received a topical application of 8 mg of BagEE, while the control group was treated with water only. Wound closure, re-epithelialization, and collagen deposition were evaluated to determine the effects of BagEE on skin healing. Results: The BagEE-treated group exhibited significantly accelerated wound healing, achieving a 99.4% closure rate by day 13 compared to the control group’s 92.8% closure rate on day 22. Additionally, wounds treated with BagEE displayed complete re-epithelialization and a well-organized skin structure. Conclusions: These findings suggest that BagEE promotes effective wound healing and shows promise as a topical agent for skin regeneration. Further studies are necessary to investigate its anti-inflammatory and wound-healing activities in both in vivo and in vitro settings.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Why Do Glioblastoma Treatments Fail?
by
Alen Rončević, Nenad Koruga, Anamarija Soldo Koruga and Robert Rončević
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010007 - 1 Feb 2025
Abstract
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most aggressive brain tumor, characterized by high recurrence rates and poor patient outcomes. Treatment failure is driven by multiple factors, including complex tumor heterogeneity, the presence of cancer stem cells, the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME), and many others. GBM’s
[...] Read more.
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most aggressive brain tumor, characterized by high recurrence rates and poor patient outcomes. Treatment failure is driven by multiple factors, including complex tumor heterogeneity, the presence of cancer stem cells, the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME), and many others. GBM’s heterogeneity underlines its ability to resist therapies and adapt to the TME. The TME, which is highly immunosuppressive and shaped by hypoxia, impairs anti-tumor immunity and limits the efficacy of immunotherapy. The blood–brain barrier (BBB) remains a major obstacle to delivering sufficient drug concentrations to the tumor by restricting the penetration of therapeutic agents. Another problem is the lack of reliable biomarkers to perform better patient stratification or even guide personalized treatments, resulting in generalized therapeutic approaches that do not adequately address GBM complexities. This review highlights the multifactorial nature of GBM treatment failure and highlights the need for a paradigm shift and innovative, personalized strategies. A deeper understanding of tumor biology and advances in translational research will be crucial to developing effective therapies and improving patient outcomes in this devastating disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Umckalin Through the Inhibition of iNOS, COX-2, Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, and MAPK Signaling in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
by
So-Yeon Oh and Chang-Gu Hyun
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010006 - 21 Jan 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Umckalin, a coumarin derivative abundantly present in the root extract of Pelargonium sidoides, is a key bioactive compound known for its antimicrobial, antiviral, antitubercular, and immunomodulatory properties. Its therapeutic potential has been extensively studied, particularly in the context of respiratory diseases.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Umckalin, a coumarin derivative abundantly present in the root extract of Pelargonium sidoides, is a key bioactive compound known for its antimicrobial, antiviral, antitubercular, and immunomodulatory properties. Its therapeutic potential has been extensively studied, particularly in the context of respiratory diseases. This study aimed to evaluate the potential of umckalin as a therapeutic agent for chronic inflammatory diseases and to elucidate its underlying mechanisms of action. Methods: Using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages as an experimental model, we investigated the inhibitory effects of umckalin on inflammatory mediators and cytokine production. We measured levels of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), and assessed the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Additionally, the regulation of MAPK signaling pathways, including JNK, p38 MAPK, and ERK, was analyzed. Results: The results demonstrated that umckalin significantly reduced the levels of NO, PGE2, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Umckalin also suppressed the expression of iNOS and COX-2, leading to decreased NO and PGE2 production. Furthermore, umckalin effectively regulated inflammatory responses by reducing the phosphorylation of MAPK signaling pathways, including JNK, p38 MAPK, and ERK. Conclusions: These findings indicate that umckalin inhibits the production of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and NO, while regulating MAPK signaling pathways, thereby suppressing the expression of iNOS and COX-2. This study highlights the potent anti-inflammatory effects of umckalin and suggests its potential as a promising candidate for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Therapeutic Approach to Inflammation and Pain)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
An Overview of Sargassum Seaweed as Natural Anticancer Therapy
by
Kelly Johanna Muñoz-Losada, Manuela Gallego-Villada and Miguel Angel Puertas-Mejía
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010005 - 20 Jan 2025
Abstract
Algae have great therapeutic value and have attracted a great deal of attention due to the abundance of bioactive compounds they contain, which may be the key to fighting diseases of various origins, such as skin cancer, breast cancer, or osteosarcoma. In this
[...] Read more.
Algae have great therapeutic value and have attracted a great deal of attention due to the abundance of bioactive compounds they contain, which may be the key to fighting diseases of various origins, such as skin cancer, breast cancer, or osteosarcoma. In this regard, global trends indicate that cancer is likely to become the leading cause of death and the main obstacle to increased life expectancy in the 21st century, which is related to multiple factors, including the various effects of climate change, which will continue to cause afflictions to human health. Then, excess exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) causes damage to DNA, proteins, enzymes, and various cellular structures and leads to the development of cancer, premature aging of the skin (wrinkles, dryness, dilation of blood vessels, and loss of collagen and elastin), or alterations of the immune system. In addition, multidrug resistance (MDR) is characterized by the overexpression of efflux pumps, such as P-glycoprotein or P-gp, that expel chemotherapeutic drugs out of the cancer cell being the main obstacle to their efficacy. Some molecules inhibit efflux pumps when co-administered with antineoplastic agents, such as glycolipids. Mycosporin-like amino acids and glycolipids isolated from Sargassum have shown an important role as potential anticancer agents. The results show that glycolipids and mycosporin-like amino acids present in brown algae of the genus Sargassum exhibit cytotoxic effects on different types of cancer, such as breast cancer, leukemia, and osteosarcoma, which is a key criterion to be considered as a natural anti-cancer strategy; but, more in-depth in vitro studies are needed to represent them at the in vivo level, as well as their validation in preclinical assays.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Prospect of (Nd3+) Complexes and Its Nanoparticles as Promising Novel Anticancer Agents in Particular Targeting Breast Cancer Cell Lines
by
Faraj Ahmad Abuilaiwi
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010004 - 14 Jan 2025
Abstract
Breast cancer is the leading cause of tumor-related death in women around much of the world and a major health burden for modern medicine. This review highlights the prospect of (Nd3+) complexes and nanoparticles as promising novel anticancer agents in particular
[...] Read more.
Breast cancer is the leading cause of tumor-related death in women around much of the world and a major health burden for modern medicine. This review highlights the prospect of (Nd3+) complexes and nanoparticles as promising novel anticancer agents in particular targeting breast cancer cell lines. This study emphasizes the therapeutic and diagnostic potentials of Nd3+-based metal complexes, especially in reversing drug resistance or enhancing targeted therapy. A comprehensive overview of diagnostic modalities underscores the imperative for the prompt identification and intervention of breast cancer. Nd3+ complexes demonstrate potential as anticancer therapeutics due to their significant cytotoxicity evidenced by their IC50 values. The research outcomes indicated that it could theoretically inhibit the growth and metastasis of cancer cell lines. Future research should focus on synthesizing novel Nd3+ complexes with enhanced bioavailability, solubility, and reduced toxicity to further advance their application.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Scheme 1
Open AccessReview
An Updated Review of the Antimicrobial Potential of Selenium Nanoparticles and Selenium-Related Toxicological Issues
by
Tainá Pereira da Silva Oliveira, Alan Kelbis Oliveira Lima and Luís Alexandre Muehlmann
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010003 - 8 Jan 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Discovered in mid-1817 by Jöns Jacob Berzelius, selenium, belonging to Group 16 of the periodic table is an essential trace element for human and animal health, due to its biocompatibility and bioavailability. Additionally, it is known for having different oxidation states, which allows
[...] Read more.
Discovered in mid-1817 by Jöns Jacob Berzelius, selenium, belonging to Group 16 of the periodic table is an essential trace element for human and animal health, due to its biocompatibility and bioavailability. Additionally, it is known for having different oxidation states, which allows it to interact with distinct chemical elements to form various compounds. Selenium exhibits two forms, organic and inorganic; the latter is known for its genotoxicity. Selenium nanoparticles have been investigated as an alternative to mitigate the toxicity of this element. With antidiabetic, antiviral, chemopreventive, and antimicrobial properties, SeNPs possess significant biomedical potential and can be synthesized using chemical, physical, or green methods, offering new solutions for combating microbial resistance and other diseases. This review discusses the historical discovery of selenium, preparation methods, the versatility of combinations for synthesis, morphological characteristics, and sizes, as well as the impact of SeNP applications obtained through different approaches against medically relevant microorganisms, particularly those exhibiting resistance to conventional antimicrobials.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
2025: A Bright Year Ahead for Future Pharmacology
by
Fabrizio Schifano
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010002 - 1 Jan 2025
Abstract
As 2024 is coming to an end, let us reflect on Future Pharmacology’s achievements to better understand what is promising to be a bright year ahead [...]
Full article
Open AccessReview
Sodium Nitroprusside: The Forgotten Vasodilator? A Brief Guide for Informed and Safe Use from Heart Failure to Hypertensive Crisis and Aortic Dissection
by
Saverio D’Elia, Rosa Franzese, Carmine Gentile, Achille Solimene, Ettore Luisi, Antonio Caiazzo, Francesco Natale, Francesco S. Loffredo, Paolo Golino and Giovanni Cimmino
Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5010001 - 26 Dec 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
Sodium nitroprusside (SNP) is a powerful vasodilator approved for treating acute hypertensive crises, acute heart failure, aortic dissection, and both controlled perioperative hypotension and perioperative hypertension. Its unique ability to cause both venous and arterial dilation makes it an invaluable option in critical
[...] Read more.
Sodium nitroprusside (SNP) is a powerful vasodilator approved for treating acute hypertensive crises, acute heart failure, aortic dissection, and both controlled perioperative hypotension and perioperative hypertension. Its unique ability to cause both venous and arterial dilation makes it an invaluable option in critical care settings. Despite concerns regarding its manageability due to potential toxicity, it is a safe choice if properly used, as highlighted by its short half-life and minimal side effects. This review aims to summarize its pharmacological properties, toxicology, and various clinical applications, particularly focusing on acute heart failure and hypertensive emergencies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
The Use of Personalized Medicine in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC): New Therapeutic Opportunities
by
Inês Mendes and Nuno Vale
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(4), 934-954; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4040049 - 20 Dec 2024
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer constitutes a significant cause of cancer-related fatalities, with a five-year survival rate of only 12%. The most prevalent form of this disease is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Given that a single therapeutic intervention has proven inadequate for the treatment of PDAC,
[...] Read more.
Pancreatic cancer constitutes a significant cause of cancer-related fatalities, with a five-year survival rate of only 12%. The most prevalent form of this disease is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Given that a single therapeutic intervention has proven inadequate for the treatment of PDAC, it is essential to identify distinct molecular signatures that could improve treatment efficacy and alleviate the economic burden on patients. Surgery is recognized as the most effective treatment option for PDAC; however, only a small percentage of patients are candidates for this procedure due to the advanced stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis. In this context, we propose to explore the biology of PDAC with a focus on microbiome, epigenetics, and genetics. Our objective is to examine the existing knowledge in these areas and to identify potential pathways for personalized medicine. This approach holds promise for advancing our understanding of PDAC development, progression, and resistance to standard therapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Biological Evaluation of 3-Aryl and/or 4-(N-Aryl)aminocoumarins Against Human Pathogens: Antileishmanial and Antiviral Activities
by
Vitor Won-Held Rabelo, Leonardo Simões de Abreu Carneiro, Luan Letieri Belem Martins, Fernando Almeida-Souza, Luciene Soares Silva, Leonardo dos Santos Corrêa Amorim, Maria Leonisa Sanchez-Nuñez, Kátia da Silva Calabrese, Paula Alvarez Abreu, Camilla Djenne Buarque and Izabel Christina Nunes de Palmer Paixão
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(4), 919-933; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4040048 - 19 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Vector-borne diseases, such as leishmaniasis and arboviral infections, represent a great challenge to human health with limited therapeutic options. In addition, sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes, affect billions of people worldwide and the emergence of new strains resistant to common antivirals,
[...] Read more.
Background: Vector-borne diseases, such as leishmaniasis and arboviral infections, represent a great challenge to human health with limited therapeutic options. In addition, sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes, affect billions of people worldwide and the emergence of new strains resistant to common antivirals, such as acyclovir (ACV), poses a serious threat to humans. In this context, coumarins have proved to be a valuable source of new derivatives with promising biological activities to fight these diseases. Methodology: 3-aryl and/or 4-(N-aryl)aminocoumarins were synthesized, and their drug-like profile was evaluated using silico tools. Their biological activity against Leishmania amazonensis promastigotes was evaluated using the MTT assay, while their antiviral activity against replication of Chikungunya, Mayaro, Zika, and type 1 Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) in Vero cells was analyzed using plaque reduction assays. Results: The in silico studies pointed to satisfactory pharmacokinetic and toxicological properties as drug candidates. Hence, their antileishmanial activity was evaluated. None of the compounds exhibited significant activity and compound 2b showed the highest activity (IC50 = 47.10 µM). We further evaluated their cytotoxicity and antiviral activity. Compound 2e showed good activity against ACV-sensitive and -resistant HSV-1 strains with EC50 values of 48.68 µM and 66.26 µM, respectively (selectivity index values of 12.5 and 9.2). Mechanism of action studies indicated that this compound acts at late steps of HSV-1 replication, such as virus egress. Conclusions: Compound 2e possesses a different mechanism of action compared to ACV and presents a promising alternative for the treatment of HSV-1 infections.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Bacterial Platform for Biopharmaceutical Production
by
Doumit Camilios-Neto, Rodolfo Ricken do Nascimento, Jonathan Ratko, Nicole Caldas Pan, Rubia Casagrande, Waldiceu A. Verri and Josiane A. Vignoli
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(4), 892-918; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4040047 - 18 Dec 2024
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a metabolically versatile opportunistic pathogen capable of surviving in a range of environments. The major contribution to these abilities relies on virulence factor production, e.g., exotoxins, phenazines, and rhamnolipids, regulated through a hierarchical system of communication, named quorum sensing (QS).
[...] Read more.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a metabolically versatile opportunistic pathogen capable of surviving in a range of environments. The major contribution to these abilities relies on virulence factor production, e.g., exotoxins, phenazines, and rhamnolipids, regulated through a hierarchical system of communication, named quorum sensing (QS). QS involves the production, release, and recognition of two classes of diffusible signal molecules: N-acyl-homoserine lactones and alkyl-quinolones. These present a central role during P. aeruginosa infection, regulating bacterial virulence and the modulation of the host immune system. The influence of this arsenal of virulence factors on bacterial–host interaction makes P. aeruginosa a highly potential platform for the development of biopharmaceuticals. Here, we comprehensively reviewed the therapeutical applications of P. aeruginosa virulence factors and quorum sensing signaling molecules on pathological conditions, ranging from infections and inflammation to cancer disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Development of New Chitosan-Based Complex with Bioactive Molecules for Regenerative Medicine
by
Natasha Maurmann, Gabriela Moraes Machado, Rafaela Hartmann Kasper, Marcos do Couto, Luan Paz, Luiza Oliveira, Juliana Girón Bastidas, Paola Arosi Bottezini, Lucas Machado Notargiacomo, Carlos Arthur Ferreira, Luciano Pighinelli, Caren Serra Bavaresco, Patricia Pranke and Myrian Brew
Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4(4), 873-891; https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4040046 - 16 Dec 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The development of new materials incorporating bioactive molecules for tissue regeneration is a growing area of interest. The objective of this study was to develop a new complex specifically designed for bone and skin tissue engineering, combining chitosan, ascorbic acid-2-magnesium phosphate (ASAP),
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The development of new materials incorporating bioactive molecules for tissue regeneration is a growing area of interest. The objective of this study was to develop a new complex specifically designed for bone and skin tissue engineering, combining chitosan, ascorbic acid-2-magnesium phosphate (ASAP), and β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP). Methods: Chitosan and the complexes chitosan/ASAP and chitosan/ASAP/β-TCP were prepared in membrane form, macerated to a particulate format, and then subjected to characterization through Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, optical and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), zeta potential, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Cell viability was evaluated through a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and with fluorescein diacetate (FDA) and propidium iodide (PI) staining in stem cells obtained from deciduous teeth. Statistical analyses were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s test. Results: The FTIR results indicated the characteristic bands in the chitosan group and the complexation between chitosan, ASAP, and β-TCP. Microscopic characterization revealed a polydisperse distribution of micrometric particles. Zeta potential measurements demonstrated a reduction in surface charge upon the addition of ASAP and β-TCP to the chitosan matrix. TGA and DSC analyses further indicated complexation between the three components and the successful formation of a cross-linked structure in the chitosan matrix. Stem cells cultured with the particulate biomaterials demonstrated their biocompatibility. Statistical analysis revealed a significant increase in cell viability for the chitosan/ASAP and chitosan/ASAP/β-TCP groups compared to the chitosan control. Conclusions: Therefore, the chitosan/ASAP complex demonstrated potential for skin regeneration, while the chitosan/ASAP/β-TCP formulation showed promise as a biomaterial for bone regeneration due to the presence of β-tricalcium phosphate.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, IJMS, Sci. Pharm., Molecules, Future Pharmacology, Biomolecules
Natural Products and Drug Discovery—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Sonia Piacente, Marta MenegazziDeadline: 30 September 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Liposome-Mediated Natural Compounds in Cancer Therapy
Guest Editors: Panayiota Christodoulou, Athanasios SkourasDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Proteins or Peptides as Effective Weapons in Antimicrobial and Cancer Therapy
Guest Editors: Nidia M. León-Sicairos, Gerardo Ramírez-RicoDeadline: 31 July 2025
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Feature Papers in Future Pharmacology 2025
Guest Editor: Fabrizio SchifanoDeadline: 31 July 2025
Special Issue in
Future Pharmacology
Dual Diagnosis: A Clinical Perspective Regarding Symptoms and Treatments
Guest Editor: Stefania ChiappiniDeadline: 31 August 2025





