Journal Description
Medical Sciences
Medical Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal, providing a platform for advances in basic, translational and clinical research, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, MEDLINE, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 12 topical sections.
Latest Articles
Visual–Motor Functions and Associated Cognitive Outcomes in Pediatric Cancer Survivors
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020041 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Pediatric cancer survivors are at high risk for visual–motor and cognitive deficits that persist throughout life. These domains are related to academic performance. The current study examined (i) whether both visuomotor and cognitive functions and (ii) whether visuomotor functions alone mediate the
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Pediatric cancer survivors are at high risk for visual–motor and cognitive deficits that persist throughout life. These domains are related to academic performance. The current study examined (i) whether both visuomotor and cognitive functions and (ii) whether visuomotor functions alone mediate the relationship between age and cognitive functions. Methods: In total, there were 210 participants (7–17 years): 70 posterior fossa tumors (Mage = 12.1 ± 3.2 years, 44% female) and 70 acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Mage = 12.3 ± 3.4 years, 45% female) survivors and 70 (Mage = 12.2 ± 3.3 years, 41% female) healthy controls. Visual motor integration, motor coordination and visual perception were assessed using the Beery VMI test. Working memory, attention and planning were assessed using CANTAB. Results: Impaired motor function is significantly more pronounced than cognitive impairment in both groups of cancer survivors (effect size from 25 to 30% for visual–motor and from 5 to 7% for cognitive functions). A multiple regression model revealed that age and visual motor functions are significant predictors of attention (in the ALL group β = −0.490, t = −4.88, p = 0.000) and working memory (in the PFT group β = 0.264, t = 2.72, p = 0.008; in the ALL group β = 0.215, t = 2.24, p = 0.028). Conclusions: In children who have experienced acute lymphoblastic leukemia and tumors of the posterior cranial fossa, visual–motor dysfunction is more pronounced than cognitive impairment. In addition, there is an association between visual–motor function disorders and working memory. These findings can be used to develop more specific rehabilitation protocols.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cancer and Cancer-Related Research)
Open AccessArticle
Role of IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α as Potential Biomarkers in Ischemic Heart Disease: A Comparative Study of Patients with CAD and Non-CAD
by
Ahmed E. Altyar, Shilpa Bhardwaj, Nehmat Ghaboura, Priya Kaushik, Sattam Khulaif Alenezi, Mohammed Jaffar Sadiq Mantargi and Muhammad Afzal
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020040 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Ischemic heart disease (CAD), a leading global health burden, arises primarily from atherosclerosis, an inflammatory condition characterized by lipid accumulation and metabolic dysregulation. The precise contribution of inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α) to CAD pathogenesis remains an area of significant research.
[...] Read more.
Background: Ischemic heart disease (CAD), a leading global health burden, arises primarily from atherosclerosis, an inflammatory condition characterized by lipid accumulation and metabolic dysregulation. The precise contribution of inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α) to CAD pathogenesis remains an area of significant research. Aim: The primary aim of this study is to examine the IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and compare them with Non-CAD individuals to evaluate their potential as diagnostic biomarkers for CAD. Methodology: A prospective observational study was conducted over 3 years, involving 100 participants divided into CAD and non-CAD groups. Blood samples were isolated and analyzed for IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α levels utilizing ELISA kits. Biochemical parameters, including lipid profiles, were also assessed. Results: This study observed significantly elevated IL-6 in patients with CAD compared with controls, while IL-2 and TNF-α levels did not reach statistical significance. The CAD group exhibited dyslipidemia characterized by elevated triglycerides and reduced HDL. Furthermore, the CAD group demonstrated alterations in biochemical parameters, including lower albumin and calcium levels, higher urea and uric acid levels, and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. These findings suggest a systemic inflammatory state and metabolic disturbances in patients with CAD. Conclusions: This study highlights IL-6 as a potential biomarker and key player in CAD pathogenesis. These findings warrant further investigation into the therapeutic potential of targeting inflammatory pathways for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Positioning of the Central Venous Catheter for Hemodialysis Using Wireless Intracavitary ECG: A Case Series and Narrative Review of the Literature
by
Simone Gianazza, Cristina Valli, Stefano Mangano, Arline Vechiu, Monica Breda, Laura Composto, Clara Claudia Sardo, Camilla Ariti and Andrea Rizzi
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020039 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aimed to evaluate the practicality and feasibility of using intracavitary electrocardiography to confirm the proper placement of a central venous catheter for hemodialysis. Central venous catheters are typically placed using an echo-guided technique based on anatomical landmarks, followed by X-ray confirmation.
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to evaluate the practicality and feasibility of using intracavitary electrocardiography to confirm the proper placement of a central venous catheter for hemodialysis. Central venous catheters are typically placed using an echo-guided technique based on anatomical landmarks, followed by X-ray confirmation. Anesthesiology guidelines recommend evaluating the intracavitary electrocardiogram during the procedure to verify the correct CVC placement. This study involved 11 patients without rhythm disturbances, in whom a central venous catheter was placed in the right internal jugular vein at our institute in 2024. The patient’s electrocardiogram was analyzed using the MAGELLANO® (Italy) device to identify changes in the P wave or QRS complex, which confirmed the CVC’s correct placement at the right cavoatrial junction. Thoracic ultrasound was used to identify the right internal jugular vein and exclude iatrogenic pneumothorax. A subsequent chest X-ray was performed to further confirm the correct placement. In addition, a non-systematic review of the most recent literature on this topic was conducted using the Database PubMed—United States National Library of Medicine. Chest X-ray consistently verified the correct placements identified by ECG-IC, with no post-procedure complications. ECG-IC is a straightforward, viable, and cost-effective technique with high sensitivity when administered by properly trained professionals. This approach, combining ultrasound-guided CVC placement in the right internal jugular vein and intracavitary ECG monitoring, can omit X-ray control in more than 90% of cases.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Safety of and Adverse Reactions to the COVID-19 Vaccine Among Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
by
Nguyen Thi Minh Thanh, Le Thi Hang, Mai Trong Hung, Tran Hoa Phuong, Nguyen Thi Phuong Lan, Mac Dang Tuan, Nguyen Xuan Bach and Nguyen Duy Anh
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020038 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of adverse reactions to the COVID-19 vaccine among pregnant and breastfeeding women and identify associated demographic and clinical factors. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted at a hospital in Hanoi, Vietnam, from November 2021 to
[...] Read more.
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of adverse reactions to the COVID-19 vaccine among pregnant and breastfeeding women and identify associated demographic and clinical factors. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted at a hospital in Hanoi, Vietnam, from November 2021 to March 2022. A total of 1204 participants, including 991 pregnant women beyond 13 weeks of gestation and 213 breastfeeding women, were recruited through convenience sampling. Data were collected using a self-administered questionnaire designed to capture demographic information and adverse reactions occurring within seven to 28 days post-vaccination. Statistical analyses, including chi-square tests, Fisher’s exact tests, and logistic regression, were performed using Stata 16.0, with the significance set at p < 0.05. Results: The most common adverse reactions were localized pain at the injection site (26.2%), dizziness and fatigue (19.2%), and fever below 39 °C (29.1%). Severe adverse reactions, such as a tight throat, coma, and premature birth, were rare. A multivariate analysis identified the significant factors associated with the adverse reactions, including age (aOR = 2.04 for participants aged 36–40 years), occupation (lower odds for farmers and business professionals), urban residency (aOR = 0.64), and a history of allergies (aOR = 1.59). Education level, number of children, and gestational age were not significantly associated with adverse events. Conclusions: The findings support the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine in pregnant and breastfeeding women, with most of the adverse reactions being mild and self-limiting.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Immunology and Infectious Diseases)
Open AccessReview
Congenital Hyperinsulinism India Association: An Approach to Address the Challenges and Opportunities of a Rare Disease
by
Jaikumar B. Contractor, Venkatesan Radha, Krati Shah, Praveen Singh, Sunil Tadepalli, Somashekhar Nimbalkar, Viswanathan Mohan and Pratik Shah
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020037 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
India’s population complexity presents varied challenges in genetic research, and while facilities have gained traction in tier-1 and -2 cities, reliance on international collaborations often delays such investigations. COVID-19 further exacerbated the issues with such sample sharing. Congenital Hyperinsulinism (CHI) is a rare
[...] Read more.
India’s population complexity presents varied challenges in genetic research, and while facilities have gained traction in tier-1 and -2 cities, reliance on international collaborations often delays such investigations. COVID-19 further exacerbated the issues with such sample sharing. Congenital Hyperinsulinism (CHI) is a rare genetic disorder of pancreatic β-cells causing hypoglycaemia in children due to abnormal insulin secretion. Given India’s high birth rate and consanguineous populations, annual CHI cases are estimated to be around up to 10,000, with up to 50% having unexplained genetic causes. Diffuse or atypical lesions in such patients often necessitate near-total-pancreatectomy, risking pancreatic exocrine insufficiency and diabetes, requiring lifelong therapy. Also, novel genetic variations complicate accurate diagnosis, risk assessment, and counselling, emphasising the need for rapid genetic assessment to prevent neurological injuries and inform treatment decisions. Despite significant efforts at many institutes, there are no dedicated organisations for CHI in India. With the implementation of the National Policy for Rare Diseases 2021, we plan to form a non-profit organisation, “Congenital Hyperinsulinism India Association (CHIA)”, comprising paediatric endocrinologists, paediatricians, geneticists, and independent researchers. The aims of this association are to generate a national database registry of patients, formulate a parent support group and CHIA consortium, design patient information leaflets, as well as foster genomic collaborations and promote clinical trials. Such steps will help sensitise the health authorities and policy makers, urging them to improve the allocation of health budgets for rare diseases, as well as empower patients and their families, contributing towards a better quality of life.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases)
Open AccessArticle
Use of Electrical Household Appliances and Risk of All Types of Tumours: A Case-Control Study
by
Shabana Noori, Abdul Aleem, Imrana Niaz Sultan, Afrasiab Khan Tareen, Hayat Ullah and Muhammad Waseem Khan
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020036 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
Introduction: The use of electrical appliances using extremely low frequency (ELF) electromagnetic fields (EMF) has increased in the past few years. These ELF MF are reported to be linked to several adverse health effects. However, only a couple of studies have been conducted
[...] Read more.
Introduction: The use of electrical appliances using extremely low frequency (ELF) electromagnetic fields (EMF) has increased in the past few years. These ELF MF are reported to be linked to several adverse health effects. However, only a couple of studies have been conducted on the association between risk of tumours and use of electronic devices using low frequency (LF) EMF. Methods: We studied the use of common household electrical appliances and suspected risk of tumours in a multi-hospital-based case-control study. In total, 316 patients were included in the final analysis. Results: The study results showed a below unity risk for most of the devices. A slight increased risk of tumour was observed for computer screen use OR: 1.13 (95% CI: 0.43–3.02) and use of microwave oven OR: 1.21 (95% CI: 0.36–4.04). We also had chance to investigate ELF MFs exposure association with tumour. Where we observed elevated odd ratios in individuals living near electricity transformer stations, with a statistically significant risk OR: 2.16 (95% CI: 1.30–3.59). However, the risk was below unity (OR: 0.98) in individuals residing close to powerlines. Conclusion: The current study serves as a pilot study of primary data and will be helpful in future epidemiological research studies on the topic in the region.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cancer and Cancer-Related Research)
Open AccessArticle
Tumour-Derived, Extracellular Microvesicles in the Treatment of Acute Renal Failure: An Experimental Study
by
Galina V. Seledtsova, Victor I. Seledtsov, Ayana B. Dorzhieva, Irina P. Ivanova, Tatiana S. Khabalova, Adas Darinskas and Alexei A. von Delwig
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020035 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This investigation compared the therapeutic efficacy of extracellular microvesicles (MVs) derived from murine L929 sarcoma cells and murine mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Methods: A mouse model of acute kidney injury (AKI) was used. Results: Both MVs from L929 cells
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This investigation compared the therapeutic efficacy of extracellular microvesicles (MVs) derived from murine L929 sarcoma cells and murine mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Methods: A mouse model of acute kidney injury (AKI) was used. Results: Both MVs from L929 cells (L929-MVs) and MSCs (MSC-MVs), unlike those obtained from murine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), enhanced survival rates in AKI mice and significantly improved kidney function. This was indicated by decreased levels of urine albumin and serum creatinine. Furthermore, treatment with L929-MVs and MSC-MVs elevated the proportions of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells while reducing the presence of pro-inflammatory CD4+CD44+ T cells in the spleens of AKI mice. Conclusions: the results highlight the potential of tumour-derived MVs to facilitate organ repair and exert cytoprotective immunomodulatory effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Nephrology and Urology)
►▼
Show Figures
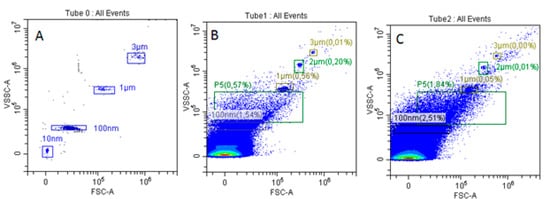
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) and Polymyalgia Rheumatica-like (PMR-like) Manifestations in Cancer Patients Following Treatment with Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab: Methodological Blurred Points Identified Through a Systematic Review of Published Case Reports
by
Ciro Manzo, Marco Isetta, Alberto Castagna and Melek Kechida
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020034 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Among rheumatologic diseases following therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), the cases of cancer patients diagnosed as having polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR), particularly with nivolumab and pembrolizumab, has been steadily rising in published reports. Objectives: We performed a systematic review of
[...] Read more.
Background: Among rheumatologic diseases following therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), the cases of cancer patients diagnosed as having polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR), particularly with nivolumab and pembrolizumab, has been steadily rising in published reports. Objectives: We performed a systematic review of published case reports with the aim of answering these questions: (1) Is PMR following therapy with nivolumab and pembrolizumab an adverse drug reaction (ADR)? (2) Is there a difference between cases of PMR following therapy with nivolumab and those following therapy with pembrolizumab? Methods: Based on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines, a comprehensive literature search in three main bibliographic databases: MEDLINE (Ovid interface), EMBASE, and COCHRANE Library was carried out on 27 December 2024. This systematic review has no registration number. Results: Data were extracted from 12 patients. Namely, 5 cases followed treatment with nivolumab and 7 with pembrolizumab. Validated scales for ADR assessment—such as Naranjo’s scale—were not used in 10 out of the 12 patients. Additionally, validated diagnostic or classification criteria for PMR were used in the majority of case reports related to nivolumab. On the contrary, clinical judgment alone was the rule in almost all case reports on pembrolizumab. Finally, the time interval between PMR manifestations and nivolumab/pembrolizumab therapy ranged from one to 14 cycles (fully compatible with pharmacokinetics). Conclusions: Our literature review highlighted significant methodological blurred lines in the categorization of PMR following therapy with nivolumab or pembrolizumab.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cancer and Cancer-Related Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study of Expression of MST3 in Myeloid Leukaemia
by
Boro Arthi, Krishnaswamy Sujatha, Sridhar Gopal, Balasubramanian Balamuralikrishnan, Meyyazhagan Arun, Pappuswamy Manikantan, Palanisamy Sampathkumar and Arumugam Vijaya Anand
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(2), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13020033 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Myeloid leukaemia (ML) is a cancer that occurs by the accumulation of abnormally multiplied myeloid cells in bone marrow, peripheral blood, and other related tissue. MST3 is a gene of the GCK family that has a role in apoptosis, along with other cellular
[...] Read more.
Myeloid leukaemia (ML) is a cancer that occurs by the accumulation of abnormally multiplied myeloid cells in bone marrow, peripheral blood, and other related tissue. MST3 is a gene of the GCK family that has a role in apoptosis, along with other cellular functions like cellular differentiation, cell cycle, metabolism, and others. Objectives: The objectives of this study were to count RBCs and WBCs, study MST3 expression in ML and control samples, and perform an in silico correlation study on the KRAS and NRAS genes. Methods: The counting of RBCs and WBCs was carried out using a hemacytometer, the expression of MST3 was studied using RT-PCR, and a correlation study was carried out using GEPIA. Results: RBC and WBC levels in ML differed from the control levels, and the expression of MST3 was found to be upregulated in ML in comparison to controls, with a 2.90–8.65-fold change, with a significant p-value > 0.05. A positive correlation in expression was also found between MST3 and KRAS and NRAS genes, with a significant r value correlation. Conclusions: From this study, it could be deduced that MST3 might have a role in ML pathogenesis, but further research is needed to study its role in the progression of the disease.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
State-of-the-Art Review on the Treatment of Axial Spondyloarthritis
by
Evripidis Kaltsonoudis, Panagiota Karagianni, Tereza Memi and Eleftherios Pelechas
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010032 - 16 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The term axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) encompasses patients with both radiographic (r-axSpA) and non-radiographic (nr-axSpA) forms of the disease. These are two entities within the same family that share many genetic and pathogenic factors, but they also have significant differences. For example, the male-to-female
[...] Read more.
The term axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) encompasses patients with both radiographic (r-axSpA) and non-radiographic (nr-axSpA) forms of the disease. These are two entities within the same family that share many genetic and pathogenic factors, but they also have significant differences. For example, the male-to-female ratio is 2:1 in r-axSpA and 1:1 in nr-axSpA. Additionally, the prevalence of the HLA-B27 gene is notably higher in r-axSpA. Early diagnosis remains an unmet need, with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) being the most important tool for diagnosis and disease monitoring. Early detection is crucial, as it allows for timely treatment, increasing the chances of preventing new bone formation and long-term structural bone damage. Various cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin-17, play active roles in the disease’s pathogenesis, although the exact mechanisms of interaction are not yet fully understood. Clarifying these mechanisms will be key to developing new classification criteria, screening methods, and more personalized, targeted therapies. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), TNF inhibitors, interleukin-17 blockers, and, more recently, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, are the most effective treatments for both radiographic and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Association Between Sociodemographic Disparities and Door to Computerized Tomography Time in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Across COVID-19 Periods in the Emergency Department: A Multi-Center Cohort Study
by
Yu-Lin Hsieh, Ching-Fang Tiffany Tzeng, Maha Khan, Andrew Shedd, Thomas Damrow, Dahlia Hassani, Matthew Danley, Jaydeep Shah, Jennifer Walker and Eric H. Chou
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010031 - 15 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death and long-term disability in the United States. The current guideline for stroke management includes a 25 min timeframe from door-to-computed tomography time (DTCT). However, sociodemographic backgrounds may impact the DTCT in acute stroke patients.
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death and long-term disability in the United States. The current guideline for stroke management includes a 25 min timeframe from door-to-computed tomography time (DTCT). However, sociodemographic backgrounds may impact the DTCT in acute stroke patients. Methods: This was a retrospective, multicenter, cohort study between January 2018 and August 2022 throughout North Texas. The primary endpoint was DTCT ≤ 25 min upon arrival to hospital for all patients suspected of acute ischemic stroke. Results: During the study period, a total of 23,364 patients were included. Only 4468 patients (19.1%) had DTCT times less than or equal to 25 min, and 16,464 patients (70.5%) had DTCT times more than 25 min. In our cohort, Black (OR 1.35; 95% CI 1.23–1.49) and Asian patients (OR 1.33; 95% CI 1.01–1.74) were more likely to have DTCT > 25 min compared to White patients. Hispanic patients (OR 1.20; 95% CI 1.07–1.34) were more likely to have DTCT > 25 min compared to non-Hispanics. Patients presenting during the COVID (OR 1.45; 95% CI 1.34–1.57) and post-COVID period (OR 1.46; 95% CI 1.30–1.65) were more likely to have DTCT > 25 min compared to the pre-COVID period. Conclusions: We demonstrated a discrepancy in DTCT time for acute ischemic stroke patients based on their race and ethnic population and an increase in DTCT time after the start of COVID-19, which has persisted after the pandemic. These diverse factors highlight the complex interplay of logistical, organizational, and healthcare challenges that have influenced DTCT time.
Full article
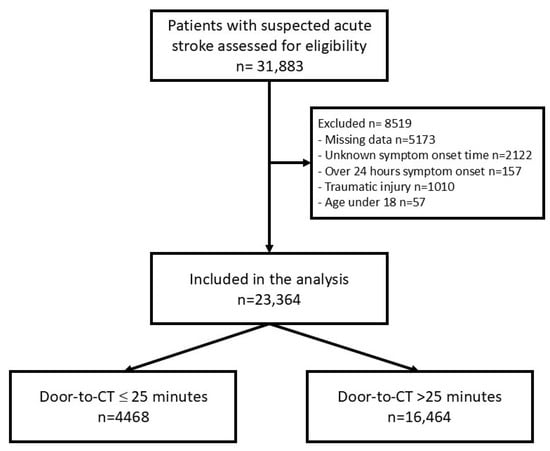
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Treatment of Vitamin D Deficiency in Decompensated Patients with Cirrhosis Is Associated with Improvement in Frailty
by
Raquel Díaz-Ruíz, Maria Poca, Eva Román, Berta Cuyàs, Irene Bañares, Ángela Morales, Elvira Hernández Martínez-Esparza, Rocío Panadero, Cristina Velasco, Marta Rapado-Castro, Irene Bretón, Rafael Bañares, German Soriano and Rita García-Martínez
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010030 - 13 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background/aim: Frailty is increasingly recognized as a relevant prognostic factor in patients with cirrhosis, regardless of liver failure. Vitamin D deficiency is frequent in these patients and has been related to frailty and sarcopenia, but the impact of its supplementation on frailty
[...] Read more.
Background/aim: Frailty is increasingly recognized as a relevant prognostic factor in patients with cirrhosis, regardless of liver failure. Vitamin D deficiency is frequent in these patients and has been related to frailty and sarcopenia, but the impact of its supplementation on frailty in cirrhosis is unknown. The aim was to evaluate the effect of vitamin D supplementation on frailty in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency. Methods: We included patients with cirrhosis who had vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency following their hospitalization for acute decompensation. Vitamin D was supplemented according to current recommendations, as were other micronutrients if necessary. Patients were followed for one year to evaluate changes at 6 and 12 months in frailty (Fried frailty index), health-related quality of life (SF-36, CLDQ) and mood (HADS). Body composition was assessed by DXA at baseline and at 12 months. Results: We included 39 patients, 27 of whom reached the 6-month follow-up. Serum vitamin D increased at 6 and 12 months (p < 0.001 compared to baseline). Fried frailty index improved at the 6-month visit (p = 0.004), and handgrip strength improved at 6 (p = 0.001) and 12 (p = 0.002) months, similarly in women and men. At 12 months, we observed an increase in body mass index, right arm lean mass and total fat mass. Conclusions: A multifactorial nutritional intervention, especially vitamin D supplementation after discharge in decompensated, vitamin D-deficient patients with cirrhosis, was associated with an improvement in frailty, muscular strength and lean muscle mass. However, the increase in fat mass strengthens the recommendation for diet, exercise and weight supervision.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Hepatic and Gastroenterology Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
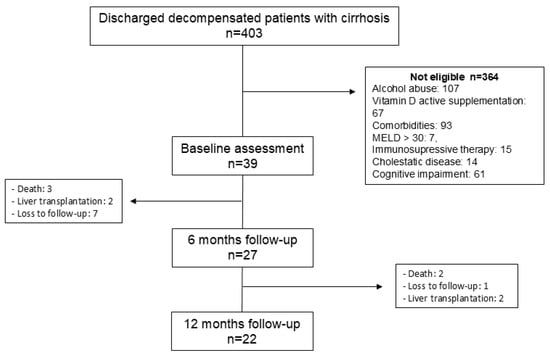
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Change in Indications and Outcomes for Stereotactic Biopsy Following Transition from Full Field Digital Mammography + Digital Breast Tomosynthesis to Full Field Synthetic Mammography + Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
by
Jose Net, Antoine Hamedi-Sangsari, Taylor Schwartz, Mirelys Barrios, Nicole Brofman, Cedric Pluguez-Turull, Jamie Spoont, Sarah Stamler and Monica Yepes
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010029 - 12 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Synthetic 2D mammography was developed to decrease radiation exposure, but to our knowledge there have been no studies evaluating the impact of implementation of full field synthetic mammography/digital breast tomosynthesis (FFSM/DBT) on indications for stereotactic biopsy. Objective: To compare indications and biopsy
[...] Read more.
Background: Synthetic 2D mammography was developed to decrease radiation exposure, but to our knowledge there have been no studies evaluating the impact of implementation of full field synthetic mammography/digital breast tomosynthesis (FFSM/DBT) on indications for stereotactic biopsy. Objective: To compare indications and biopsy outcomes for stereotactic biopsy for full field digital mammography (FFDM/DBT) to those of FFSM/DBT. Methods: Retrospective chart review of stereotactic biopsies performed from July 2014 to September 2018. Reports were reviewed and indication for biopsy, lesion size, and final pathology were recorded. Comparison between the two groups following transition to FFSM/DBT in 2016 was performed. Results: 66 of 361 stereotactic biopsies performed in the FFDM/DBT group were malignant (PPV 18.3%), compared to 60 of the 391 biopsies performed in the FFSM/DBT group (PPV 15.4%) with no significant difference in PPV (p = 0.281). There were statistically significant changes in indications for biopsies after transitioning to FFSM/DBT: with a decrease in calcifications referred for biopsy (68.03% vs. 89.75%; p < 0.001), and a statistically significant increase in referral of masses (10.74% vs. 4.43%; p < 0.001), asymmetries (15.60% vs. 5.26%; p < 0.001), and architectural distortion (5.63% vs. 0.55%; p < 0.001). PPV across all indications (21.8% in FFSM/DBT vs. 20.3% in FFDM; p = 0.213), and invasive cancer yield (5.63% vs. 3.32%; p = 0.129) remained comparable following transition to FFSM/DBT without statistically significant differences. Conclusions: Following transition to FFSM/DBT, statistically significant shifts in indications for biopsies were observed with a decrease in referral of calcifications and an increase for masses, asymmetries and architectural distortions. PPV for stereotactic biopsy was not significantly different and cancer yield across all indications remained similar, with an increase in invasive cancer diagnosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cancer and Cancer-Related Research)
►▼
Show Figures
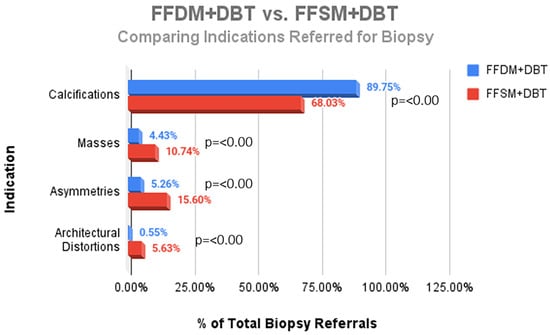
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Protective Effect of Daily Physical Activity Against COVID-19 in a Young Adult Population on Reunion Island
by
Camille Cazeneuve, David Couret, Gregorie Lebeau, Wildriss Viranaicken, Marie-Eve Mathieu and Florian Chouchou
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010028 - 12 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The global fight against pandemics is a major public health issue. Epidemiological studies showed a reduced risk of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity with the practice of regular physical activity (PA) in clinical populations. Here, we investigated the effect of PA against
[...] Read more.
The global fight against pandemics is a major public health issue. Epidemiological studies showed a reduced risk of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity with the practice of regular physical activity (PA) in clinical populations. Here, we investigated the effect of PA against COVID-19 in a young general population. Methods: Two hundred ninety volunteers over 18 years old from Reunion Island responded to an online survey concerning sociodemographic, lifestyle and clinical information. Daily PA was studied using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire short version (IPAQ) and classified by overall score and intensities of PA. Results: Among 290 responders [179 women, median age = 27.5 years (interquartile range = 21.3 years)], 141 (48.6%) reported COVID-19 infection. Multivariate logistic analysis adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, chronic disease and alcohol consumption showed that the number of days per week of regular intense PA was independently associated with a low risk of COVID-19 infection [odds ratio (OR) 0.86; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.24 to 0.99; p = 0.030], while regular moderate PA was not [OR 1.10; 95%CI 0.97 to 1.23; p = 0.137]. Conclusions: In a population of young adults, regular intense PA could offer a protective effect against COVID-19. Additional research is required to confirm this association in various viral infections and elucidate the fundamental mechanisms involved.
Full article
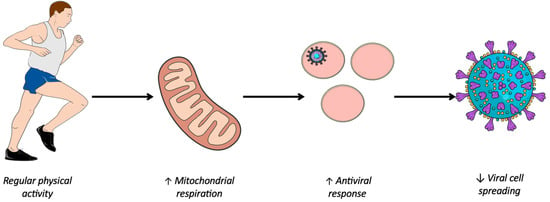
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
FGF-23 as a Biomarker for Carotid Plaque Vulnerability: A Systematic Review
by
Joana Oliveira-Sousa, Mariana Fragão-Marques, Luís Duarte-Gamas, Hugo Ribeiro and João Rocha-Neves
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010027 - 10 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Carotid artery disease is a condition affecting 3% of the general population which significantly contributes to the development of cerebrovascular events. Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 (FGF-23) is a hormone that has been linked to atherosclerosis and increased cardiovascular risk, including stroke and myocardial
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Carotid artery disease is a condition affecting 3% of the general population which significantly contributes to the development of cerebrovascular events. Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 (FGF-23) is a hormone that has been linked to atherosclerosis and increased cardiovascular risk, including stroke and myocardial infarction. This review explores the association of FGF-23 with carotid artery disease progression in an endarterectomy clinical context. Methods: Based on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), a search was performed relying on MEDLINE, Scopus and Web of Science, identifying publications focused on the correlation between serum FGF-23 and carotid artery disease. Assessment of study quality was made using National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Study Quality Assessment Tool (NHLBI). Results: Three observational studies, comprising 1039 participants, were included. There was considerable heterogeneity among the populations from the different studies. Elevated FGF-23 levels were consistently associated with unstable plaque features, including intraplaque neovascularization, as identified through Superb Microvascular Imaging (SMI). Plasma levels of inflammatory mediators, such as Interleukin-6 (Il-6), Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1), and Osteoprotegerin (OPG), positively correlated with carotid artery disease, but their link to unstable plaques is conflicting. None of the studies investigated clinical complications following carotid endarterectomy. Conclusions: FGF-23 is a potential biomarker for plaque vulnerability in carotid disease. Despite promising findings, limitations such as small sample sizes and lack of longitudinal data suggest the need for larger and more diverse studies to improve risk stratification and inform personalized treatment strategies for carotid atherosclerosis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Body Integrity Dysphoria (BID): Survey of Experts and Development of a Diagnostic Guideline
by
Erich Kasten
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010026 - 3 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
People who suffer from body integrity dysphoria (BID) feel a strong need to be disabled. The most common desire is for amputation or paralysis. Objectives: This study aims to gather the opinion of experts on which types of disabilities are included in BID,
[...] Read more.
People who suffer from body integrity dysphoria (BID) feel a strong need to be disabled. The most common desire is for amputation or paralysis. Objectives: This study aims to gather the opinion of experts on which types of disabilities are included in BID, which therapies are useful and whether those affected should be supported in obtaining a disability. Methods: A questionnaire with 62 items and a flow chart were developed and sent to experts who have published work with regard to BID. Participants: 22 experts from 11 countries, mostly with an academic title and with an average age of 48.5 years, responded. Results: As expected, amputations and paralysis were clearly attributed to BID, other disabilities (toothlessness, incontinence, diabetes) received rather uncertain or negative scores. On average, those affected were not classified as mentally or psychiatrically ill. Neurological misconnection was considered the most likely cause. Experts did not think it was helpful to inform the health system or even the police about the desire to be disabled. Almost all experts supported the surgical solution of amputation by doctors. All participants believed that BID patients are aware of the limitations imposed by the desired disability. Finally, a flow chart is presented for diagnosis and therapy. Conclusions: The experts assume that the surgical solution is currently acceptable if it has been proven that the BID-affected person does not suffer from another mental disorder, there is a high level of suffering due to BID, other therapies have not been of any use and it is clear that the quality of life will actually increase as a result of achieving the disability.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Thermo-Ablative Fractional CO2 Lasers Combined with 1540 nm Wavelengths Is a Promising Treatment Option in Stress Urinary Incontinence
by
Maurizio Filippini, Sara Elmi, Jessica Sozzi, Laura Pieri, Irene Fusco, Tiziano Zingoni and Pablo González-Isaza
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010025 - 1 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is a common and often under-reported condition that significantly impacts quality of life. SUI is more than just a physical issue; it can also affect social interactions, mental health, and emotional well-being due to the embarrassment and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is a common and often under-reported condition that significantly impacts quality of life. SUI is more than just a physical issue; it can also affect social interactions, mental health, and emotional well-being due to the embarrassment and limitations it can cause. SUI is often acquired during pregnancy and childbirth as a result of pelvic floor muscle weakness. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of an innovative dual-wavelength laser system (CO2 + 1540 nm) in SUI management. Methods: A total of 56 women affected by SUI were enrolled in this study. Half of the patients were treated with CO2 alone, while the other half were treated with the combination of CO2 + 1540 nm wavelengths. The patients were split into four groups based on the type of treatment they received and their menopausal status. Data were acquired at baseline and at various follow-ups (T1, T2, and T3, respectively, after the first, second, and third treatment). The Visual Analog Scale (VAS) (score 0–10) was used. Cystoscopic images were acquired before and at the end of the laser treatment cycle. Results: At the end of the treatment, the patients in each group were very satisfied, on average. In each group, the treatment led to a statistically significant improvement in the SUI VAS score between baseline and follow-up after the first treatment; in both groups 3 and 4, the treatment led to a significant change in the dryness score, both from baseline to T1 (p < 0.05) and also for T2 and T3 compared to baseline. Finally, cystoscopic photos showed an evident increase in mucosa epithelial thickness after the laser treatment cycle. Conclusions: The use of a dual-wavelength laser system (CO2 + 1540 nm) was proven to be well tolerated and safe, with promising outcomes in reducing SUI symptoms, especially in non-menopausal patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gynecology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing Breast Cancer Awareness Among Women in Al Baha, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the Breast Cancer Awareness Measure (BCAM)
by
Mohammad A. Albanghali, Rawan K. Alnemari, Rhaff B. Al Ghamdi, Fatma Alzahraa M. Gomaa, Taif A. Alzahrani, Alya S. Al Ghamdi, Batol M. Albanghali, Yasser M. Kofiah, Eltayeb M. Alhassan and Basim A. Othman
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010024 - 1 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Breast cancer (BC) awareness and preventive practices are critical for the early detection and effective management of the disease. This study aimed to assess the level of BC awareness among women residing in Al Baha, Saudi Arabia. Methods: A cross-sectional study was
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Breast cancer (BC) awareness and preventive practices are critical for the early detection and effective management of the disease. This study aimed to assess the level of BC awareness among women residing in Al Baha, Saudi Arabia. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted using the Breast Cancer Awareness Measure (BCAM) survey tool to evaluate BC awareness among female residents of Al Baha between June and July 2023. The sample was obtained through the snowball sampling technique. Results: A total of 1007 women participated in the study, with a mean age of 29 ± 10.9 years. Overall awareness of BC warning signs and risk factors was low, with 45% of participants demonstrating poor awareness. Significant positive associations were found between BC awareness and factors such as level of education (p = 0.020), employment status (p = 0.023), field of study for students (p < 0.0001), and average monthly family income (p = 0.001). Furthermore, 75% of participants rarely or never practiced breast self-examination, and only 37% of those invited to the Ministry of Health’s screening program had attended. Conclusions: The results highlight a significant lack of awareness and knowledge about BC among women in Al Baha. These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted educational initiatives and awareness campaigns to address this knowledge gap and promote preventive practices.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on the Prevalence and Incidence of Enteric Protozoa in a Spanish Tertiary-Care Hospital and a Referral Center for Tropical Diseases, 2019–2023
by
Alfredo Maldonado-Barrueco, Fernando de la Calle-Prieto, Marta Díaz-Menéndez, Marta Arsuaga, Julio García-Rodríguez and Guillermo Ruiz-Carrascoso
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010023 - 1 Mar 2025
Abstract
Objetive: The aim of this study was to describe the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with symptoms of enteric protozoa (EP), including Blastocystis spp., Dientamoeba fragilis, Giardia lamblia, Cryptosporidium spp., Entamoeba histolytica, and Cyclospora cayetanensis,
[...] Read more.
Objetive: The aim of this study was to describe the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with symptoms of enteric protozoa (EP), including Blastocystis spp., Dientamoeba fragilis, Giardia lamblia, Cryptosporidium spp., Entamoeba histolytica, and Cyclospora cayetanensis, in the overall population and in patients who were consulted at a National Referral Center for Imported Tropical Diseases (NRCITD patients) from a healthcare area in Madrid (Spain). Method: Data on patients with positive RT-PCR results for EP were collected. The periods analyzed were prepandemic (P0, 1 April 2019–31 March 2020), and the first (P1, 1 April 2020–31 March 2021), second (P2, 1 April 2021–31 March 2022), and third (P3, 1 April 2022–31 March 2023) pandemic years. We compared the prevalence, median age, absolute incidence (EP per 100,000 population of each period), and patient profile (NRCITD vs. non-NRCITD) during the study periods using Fisher’s test (p < 0.05) and the T-test (p < 0.001). Results: During P0, 24.8%, [95% CI: 23.9–25.6] of patients tested for EP RT-PCR were positive, 22.6% [95% CI: 21.5–23.7] were positive in P1, 20.4%, [95% CI: 19.5–21.3] were positive during P2, and 20% [95% CI: 19.2–20.9] of patients tested during P3 were positive. During the study, there was no difference in the median ages. The prevalence and absolute incidence of EP showed a decreasing trend during the pandemic for the NRCITD and non-NRCITD patients (p < 0.05). Conclusion: Blastocystis spp. and D. fragilis showed a lower decrease in prevalence during P1 (p > 0.05) due to the higher detection of colonized patients during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. However, G. lamblia and Cryptosporidium spp. showed the highest decrease in prevalence and absolute incidence during P2 (p < 0.05) because of the NPIs implemented during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. The NTRCID patients showed a higher prevalence of Blastocystis spp. than the non-NTRCID patients during every period studied (p < 0.001). E. histolytica and C. cayetanensis showed a homogeneous trend.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Immunology and Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Examination of the Relationship Between the Number of Births with the Symptoms of Urinary Incontinence and Low Back Pain Postpartum in Greek Women
by
Eleni Katsouli, Eleni-Alexandra Karathanasi, Eleftheria Ntalagianni, Themistoklis-Marios Terpos and Anna Christakou
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13010022 - 1 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Urinary incontinence and low back pain are often present during pregnancy and after childbirth. The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between the number of children with the occurrence of urinary incontinence and low back pain after pregnancy in
[...] Read more.
Background: Urinary incontinence and low back pain are often present during pregnancy and after childbirth. The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between the number of children with the occurrence of urinary incontinence and low back pain after pregnancy in the Greek population. Materials and Methods: Seventy-one Greek women (M = 35.0 age, SD = ±4.3) with specific inclusion criteria completed just once the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire and the Oswestry Disability Questionnaire after five years from childbirth. Results: A total of 28.2% of the participating women experienced urinary incontinence, and 38% experienced low back pain after pregnancy. No relationship has been found between urinary incontinence and the number of births (r = 0.062, p = 0.609) and low back pain with the number of births (r = −0.076, p = 0.529). Statistically significant correlations were found between urinary incontinence and low back pain (r = 0.33, p < 0.01) and the urinary incontinence and the maternal age at first delivery (r = −0.264, p = 0.026) in women who underwent a vaginal delivery in second birth had fewer urinary incontinence symptoms and increased low back pain. Conclusions: Few correlations emerged in the present study. Future research is necessary to be conducted to examine the relationship between postpartum women’s demographic data, urinary incontinence, and low back pain.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Cancers, Medicines, Medical Sciences, Cells, Pharmaceuticals, Biology
Advances in Anti-Cancer Drugs: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Armando Varela-Ramirez, Elisa Robles-Escajeda, Blanca E. Ruiz-Medina, Patricia Talamás-Rohana, Rachid SkoutaDeadline: 31 August 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Medical Sciences
The Impact of Temporomandibular Disorders on the Wellbeing
Guest Editor: Oana AlmasanDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Medical Sciences
Advances in the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Collection Editor: Maria Liguori
Topical Collection in
Medical Sciences
Advances in Skin Wound Healing
Collection Editors: Heiko Sorg, Daniel J. Tilkorn