-
 Genotype-by-Environment Interactions and Response to Selection for Milk Production Traits in Lacaune Sheep from Greece and France
Genotype-by-Environment Interactions and Response to Selection for Milk Production Traits in Lacaune Sheep from Greece and France -
 Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated with Tail Length and Tail Kinks in Piglets
Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated with Tail Length and Tail Kinks in Piglets -
 Characterizing the Roles of Life Stage and Season on the Prevalence of Select Viral Pathogens in Acheta domesticus Crickets on a Commercial Cricket Farm in the United States
Characterizing the Roles of Life Stage and Season on the Prevalence of Select Viral Pathogens in Acheta domesticus Crickets on a Commercial Cricket Farm in the United States
Journal Description
Veterinary Sciences
Veterinary Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on veterinary sciences published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, PubAg, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Veterinary Sciences) / CiteScore - Q2 (General Veterinary)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.0 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.2 (2023)
Latest Articles
A Preliminary Evaluation of the Comparative Efficacy of Gel-Based and Oil-Based CBD on Hematologic and Biochemical Responses in Dogs
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 342; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040342 (registering DOI) - 7 Apr 2025
Abstract
Cannabidiol (CBD) has gained popularity in veterinary medicine for its potential to alleviate stress, pain, and inflammation in dogs. However, its oral administration is limited by hydrophobicity, variable absorption, and extensive first-pass metabolism, which requires optimized delivery methods to enhance efficacy. This study
[...] Read more.
Cannabidiol (CBD) has gained popularity in veterinary medicine for its potential to alleviate stress, pain, and inflammation in dogs. However, its oral administration is limited by hydrophobicity, variable absorption, and extensive first-pass metabolism, which requires optimized delivery methods to enhance efficacy. This study investigated the effects of daily oral supplementation of CBD oil and CBD gel (each at 4 mg/kg), compared to a placebo, over 14 days in shelter dogs subjected to solitary confinement-induced stress. Both CBD formulations appeared safe under the study conditions, with no adverse effects on hematological and biochemical parameters. Post-stress cortisol levels were significantly lower in CBD-treated groups compared to controls, with CBD-infused gel showing a pattern toward greater attenuation. Multivariate analysis revealed distinct blood profile shifts in CBD-treated dogs, with PCA loadings indicating associations between CBD supplementation and lymphocyte percentages and IgG levels. These findings support gel-based CBD as a promising strategy for stress modulation in dogs. Further studies should explore its pharmacokinetics and long-term immune effects to optimize veterinary applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Biomedical Sciences)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Diagnostic Accuracy of Lung Ultrasound in Rabbit Subclinical Lung Lesions
by
Roberto Sargo, Inês Tomé, Filipe Silva and Mário Ginja
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 340; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040340 (registering DOI) - 7 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rabbits are commonly affected by subclinical lung diseases. Computed tomography (CT) is the gold standard for diagnosing rabbit lung diseases but is not widely available and requires anesthesia, delaying diagnosis. Lung ultrasound (LUS) has emerged as a radiation-free, bedside diagnostic tool in human
[...] Read more.
Rabbits are commonly affected by subclinical lung diseases. Computed tomography (CT) is the gold standard for diagnosing rabbit lung diseases but is not widely available and requires anesthesia, delaying diagnosis. Lung ultrasound (LUS) has emerged as a radiation-free, bedside diagnostic tool in human and veterinary medicine, though its use in rabbit medicine is not routine. This study aimed to evaluate LUS for detecting subclinical lung lesions in rabbits. Thirty healthy, five-month-old male New Zealand white rabbits underwent lung ultrasound, exploring four regions in each hemithorax, followed by thoracic CT under sedation with midazolam and butorphanol. The ultrasound images were scored as positive or negative, and the CT exams were assessed for aeration using threshold masks. The results showed that 63% of rabbits had one or more affected regions in the ultrasound images, and 19% of the regions were positive. CT identified 54% of the regions as positive for poorly aerated tissue, with 26/30 rabbits showing at least one positive region. The sensitivity and specificity of LUS were 33.33% and 93.48%, respectively, with an accuracy of 67.92% for detecting subclinical lesions. While LUS demonstrated a high specificity, its sensitivity was low compared to CT, highlighting the need for further refinement in its use for rabbit respiratory disease diagnosis.
Full article
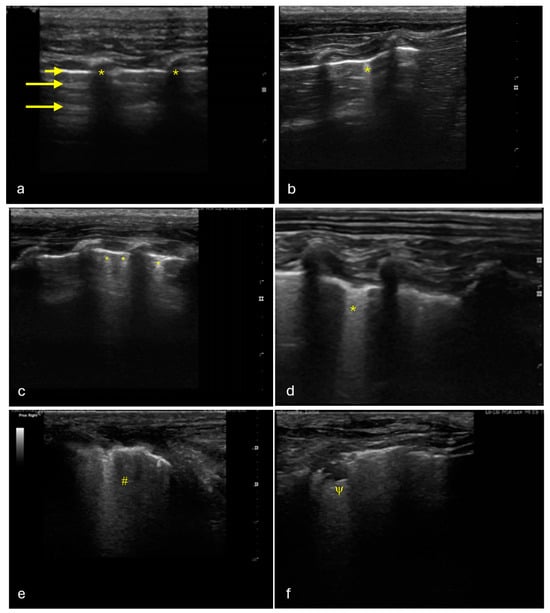
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Yellow Fever in Non-Human Primates: A Veterinary Guide from a One Health Perspective
by
Remco A. Nederlof, Tommaso Virgilio, Hendrickus J. J. Stemkens, Luiz C. C. Pereira da Silva, Daniela R. Montagna, Abdussamad M. Abdussamad, John Chipangura and Jaco Bakker
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 339; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040339 (registering DOI) - 6 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Yellow fever (YF) causes severe morbidity and mortality in Africa and South America. It is an arthropod-borne viral disease endemic to tropical regions of Africa and South America. Yellow fever virus (YFV) is transmitted by mosquitoes and frequently affects both non-human primates (NHPs)
[...] Read more.
Yellow fever (YF) causes severe morbidity and mortality in Africa and South America. It is an arthropod-borne viral disease endemic to tropical regions of Africa and South America. Yellow fever virus (YFV) is transmitted by mosquitoes and frequently affects both non-human primates (NHPs) and humans. Neotropical primates (NTPs) are generally more severely afflicted by YFV than African primates. Asian primates appear not to be susceptible to this disease. Susceptibility varies among NTP species: asymptomatic infections are described in some NTP species, whereas severe epizootic mortality events are described in others. The genus Alouatta (howler monkeys) is considered to be the most susceptible among the NTPs. Epizootic events resulting in the death of thousands of NTPs have been recorded in recent history. As a result, YFV poses a threat to the survival of some NTP species. In most cases, NTPs are found dead without showing prior clinical signs. In cases where clinical signs are observed, they are mostly non-specific. Due to their high susceptibility, epizootic events in NTPs are used as epidemiological predictors for human YF outbreaks. YFV infection may be diagnosed by means of virus isolation, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, serology, histopathology, or immunohistochemistry. Animals that survive the disease develop neutralizing antibodies to YFV. Currently, no specific treatment is available. Sustained YF control strategies must rely on surveillance and accurate diagnostics to allow for early detection of outbreaks and rapid implementation of control measures. Prophylaxis should be based on a One Health perspective that recognizes the intricate interplay between human health, primate health, and the environment. Vaccines for YF are available, with the human 17DD vaccine effectively preventing disease in primates. However, mitigation strategies continue to rely more and more on vector control, preferably using eco-friendly methods. Climate change and human activities, and their impact on local ecology, are assumed to increase the risk of YF transmission in the next decades.
Full article
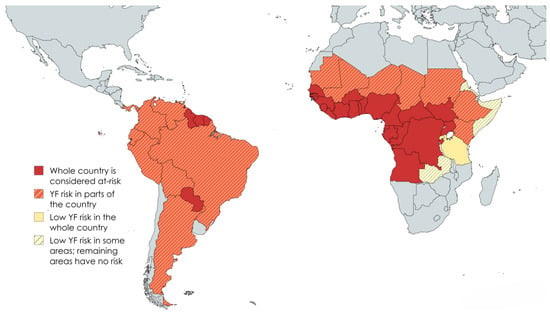
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Morphometric Analysis of the Common Raccoon Dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) Teeth in Lithuania
by
Eugenijus Jurgelėnas, Sigita Kerzienė, Linas Daugnora and Daniel Makowiecki
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 338; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040338 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
Sex identification is often challenging, especially when only skeletal remains are available. While previous research has primarily focused on skull measurements, dental traits have received less attention. This study aimed to measure the upper and lower canines, molars, and tooth rows of raccoon
[...] Read more.
Sex identification is often challenging, especially when only skeletal remains are available. While previous research has primarily focused on skull measurements, dental traits have received less attention. This study aimed to measure the upper and lower canines, molars, and tooth rows of raccoon dogs in Lithuania to examine sexual dimorphism and analyze the correlation between different teeth and tooth row measurements. A total of 90 skulls with lower jaws of adult raccoon dogs were examined, including 55 males and 35 females. Osteometric analysis followed standard protocols, with canine measurements adapted using a method tailored to the dentition of carnivorous species. Of all the study measurements, the canine teeth demonstrated the most significant sex differences. The correlation analysis showed a strong correlation (p < 0.001) between the dimensions of the upper molars P4, M1, and M2. The upper tooth rows were strongly correlated (p < 0.001) with the dimensions of the P4 and canines. Lower molar correlations were weaker than upper ones, and lower tooth rows showed less correlation with tooth measurements. These findings indicate that molars and tooth rows are not reliable for sex determination in raccoon dogs. However, the observed sexual dimorphism in canine teeth may offer insights for future zooarchaeological and comparative anatomical studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Anatomy, Histology and Pathology)
Open AccessArticle
Serological Investigations on Environmental Allergens Triggering Allergic Dermatitis in Dogs from Western Romania
by
Alexandra Ban-Cucerzan, Diana Obistioiu, Kalman Imre, Adriana Morar, Tiana Florea, Sebastian-Alexandru Popa, Răzvan-Tudor Pătrînjan, Miruna Șerdean and Emil Tîrziu
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 337; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040337 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
This study focused on identifying the environmental allergens causing allergic dermatitis in 250 dogs from Western Romania. Among the 250 dogs tested, 43% (107) exhibited significant allergic reactions (IgE levels greater than 2 kU/L), particularly in Maltese, French Bulldogs, Golden Retrievers, and West
[...] Read more.
This study focused on identifying the environmental allergens causing allergic dermatitis in 250 dogs from Western Romania. Among the 250 dogs tested, 43% (107) exhibited significant allergic reactions (IgE levels greater than 2 kU/L), particularly in Maltese, French Bulldogs, Golden Retrievers, and West Highland White Terriers. The highest reactivity was observed to house dust mites (Dermatophagoides farinae, 91%), rye pollen (45%), and flea allergen Ctef 1 (15%). Statistical analyses revealed significant correlations between breed, sex, and living environment. Males exhibited a higher susceptibility to allergies (p < 0.001), whereas dogs that spent most of their time indoors were significantly more susceptible to allergic diseases than their mostly outdoors counterparts (p < 0.05). Additionally, dogs under two years old, especially those on a dry food diet, had an elevated risk of developing allergies (p < 0.01). Clinical manifestations included pruritus (60%), otitis externa (42%), and specific skin lesions (66%). The study underscores the role of environmental and dietary factors in the development of allergies in dogs. However, financial limitations related to allergy testing kits restricted the sample size, highlighting the need for further, more comprehensive research to enhance the generalizability of these findings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnosis and Treatment of Skin Diseases in Small Animals)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Determination of Natural Blood Plasma Melatonin Concentration of Tsigai Ewes Characteristic for Gestation and Early Postpartum Period Between Autumnal Equinox and Winter Solstice
by
András Gáspárdy, László Gulyás, Ida Polland, Alán Alpár, Sándor György Fekete and Levente Harmat
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 336; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040336 (registering DOI) - 5 Apr 2025
Abstract
The aim of this investigation was to measure the natural nocturnal plasma melatonin concentration in gestating and fresh ewes. Studies in humans showed that maternal melatonin had a significant increase as pregnancy progressed and then decreased after birth. Two studies conducted in sheep
[...] Read more.
The aim of this investigation was to measure the natural nocturnal plasma melatonin concentration in gestating and fresh ewes. Studies in humans showed that maternal melatonin had a significant increase as pregnancy progressed and then decreased after birth. Two studies conducted in sheep so far, considering the entire gestation, have led to conflicting results. The breed of 16 pregnant ewes selected for the research was the Tsigai. Blood samples were taken into EDTA vacutainers predetermined times a night at different stages of their gestation. The RIA method was used to determine the melatonin concentrations. For estimation of its variations during gestation, population genetic statistics was applied. It was found that the average plasma melatonin concentration of 134 pg mL−1 is characteristic for the investigated period, and that it rises between the autumnal equinox and the winter solstice. Secondly, it was revealed that the average melatonin concentration adjusted for midnight is 162.4 pg mL−1, and its moderate variation is characteristic for the night. The investigation showed that there is no connection between the plasma melatonin concentration of the ewes and their gestational age in the Tsigai breed in Middle Europe. Our result is consistent with the results of single studies in sheep and donkey, in contrast to human observations. With regard to the nocturnal plasma melatonin, the concentration is reduced at the same level (30 pg mL−1) in ewes and lambs during the early postpartum period without nightly fluctuation. The expelled placenta, the constant vigilance between the mother and her lamb, and the opposition between melatonin and prolactin may provide a plausible explanation for this.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental Impact on the Reproductive Parameters of Domestic Animals)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Smallholder Cattle Farmers’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Toward Rabies: A Regional Survey in Kazakhstan
by
Nurbek Ginayatov, Zukhra Aitpayeva, Izimgali Zhubantayev, Leila Kassymbekova, Assylbek Zhanabayev, Gulmira Abulgazimova, Raikhan Arynova, Alim Bizhanov, Assiya Mussayeva, Maxat Berdikulov, Marat Aisin, Zaure Sayakova, Spandiyar Tursunkulov, Nurkuisa Rametov, Ainur Akhmadiyeva, Aigul Bulasheva, Nurgul Jussupbekova, Olzhas Yeskhojayev, Gulnara Baikadamova, Kaissar Kushaliyev, Nadezhda Burambayeva and Arman Issimovadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 335; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040335 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rabies remains a significant public health and economic concern in Kazakhstan, particularly in rural livestock-farming communities. This study aimed to assess the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAPs) related to rabies among livestock farmers in the Aktobe and Oral regions of West Kazakhstan. A
[...] Read more.
Rabies remains a significant public health and economic concern in Kazakhstan, particularly in rural livestock-farming communities. This study aimed to assess the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAPs) related to rabies among livestock farmers in the Aktobe and Oral regions of West Kazakhstan. A cross-sectional survey was conducted between April and August 2022, involving 688 randomly selected participants. The data were collected through structured interviews and analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics. The findings revealed that 89% of respondents were aware of rabies, yet significant knowledge gaps existed regarding clinical signs, transmission, and prevention. While 87% recognized the importance of rabies vaccination in dogs, 81% were unaware of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for cattle, and 72% lacked knowledge of PrEP for humans. Awareness of the post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) regimen was significantly higher in the Aktobe region (p < 0.002). Attitudinal differences were observed, with the Oral region participants exhibiting more favorable perceptions of rabies control programs (p < 0.01). Additionally, the χ2 test revealed that the proportion of female respondents (p < 0.02), those with school-aged dependents (p < 0.003), respondents owning both exotic and indigenous cattle breeds (p < 0.002), and those possessing more than five cattle (p < 0.025) was statistically different in the Oral region. Practices such as free grazing, lack of protective equipment use, and improper carcass disposal were identified as potential risk factors for rabies transmission. This study highlights the need for targeted educational initiatives to improve rabies awareness and promote safer livestock management practices. Enhancing veterinary surveillance, strengthening community engagement, and expanding vaccination efforts could mitigate rabies transmission risks.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Biosecurity Practices in Portuguese Small Ruminant Farms: Current Status and Future Directions
by
Maria Alavedra, Dina Moura, Beniamino Cenci-Goga, Sónia Saraiva, Filipe Silva, Isabel Pires, Cristina Saraiva, Ana Cláudia Coelho and Juan García-Díez
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 334; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040334 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Biosecurity is essential in livestock farming to prevent the spread of diseases, ensure animal welfare, and maintain farm sustainability. In Portugal, small ruminant farms are predominantly extensive and small-scale, and most of them are familiar, especially in the northern and inland regions. Thus,
[...] Read more.
Biosecurity is essential in livestock farming to prevent the spread of diseases, ensure animal welfare, and maintain farm sustainability. In Portugal, small ruminant farms are predominantly extensive and small-scale, and most of them are familiar, especially in the northern and inland regions. Thus, biosecurity implementation on these farms is low due to factors such as an aging livestock farmer population, poor training, limited veterinary support, and economic constraints. This study, the first to assess biosecurity on Portuguese small ruminant farms, evaluated compliance levels and the influence of sociodemographic factors. A cross-sectional study was conducted between July 2023 and April 2024, through structured interviews with 276 farmers. A 32-question checklist covering nine biosecurity categories was used to assess compliance. The results revealed poor implementation of key biosecurity measures, particularly cleaning and disinfection, quarantine protocols, and visitor control. Inadequate premises infrastructure, including the absence of quarantine areas, isolation facilities for sick animals, and farrowing rooms, further hampered disease prevention. Compliance was influenced by farmers’ age, education level, herd size, and production. Larger farms, particularly dairy farms, demonstrated better biosecurity practices, likely due to better management and infrastructure. This study highlights the challenges of implementing biosecurity measures on small-scale, extensive farms and argues that standardized plans are ineffective. Instead, region- and farm-specific strategies are needed, considering the socioeconomic realities of farmers. Improving farmers’ education and access to veterinary services is crucial. Furthermore, public policies should provide financial incentives and educational programs to improve biosecurity without compromising farm viability. Strengthening biosecurity on small ruminant farms is vital to protecting animal and public health and ensuring the long-term sustainability of rural communities in Portugal.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Potential Therapeutic Effect of ZnO/CuO Nanocomposite as an Acaricidal, Immunostimulant, and Antioxidant in Rabbits
by
Shimaa R. Masoud, Said I. Fathalla, Sherif M. Shawky, Hanem El-Gendy, Mahboba A. Z. Alakhras, Rashed A. Alhotan, Anam Ayyoub, Shaimaa Selim, Khaled Defallah Al-Otaibi and Ahmed M. A. El-Seidy
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 333; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040333 - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The present study aimed to identify a safe and novel approach using zinc oxide/copper oxide nanocomposites (AZ) to enhance growth parameters, immunity, and fight Sarcoptic mange in vitro and in vivo in rabbits. In vitro: the acaricidal activity of AZ was assessed at
[...] Read more.
The present study aimed to identify a safe and novel approach using zinc oxide/copper oxide nanocomposites (AZ) to enhance growth parameters, immunity, and fight Sarcoptic mange in vitro and in vivo in rabbits. In vitro: the acaricidal activity of AZ was assessed at concentrations of AZ-25: 2.5% w/w AZ/molasses, AZ-125: 12.5% w/w AZ/molasses, and controls (normal saline, molasses, and Ivermectin) every hour for seven hours under a stereoscopic microscope. In vivo: involved 40 rabbits (10 replicates/group). G1 served as the control negative group (normal un-infected rabbits), G2 served as the control negative group (infected rabbits), the animals in the G3 group were given a combination of AZ (40 mg/kg body weight (BW)) and molasses (5 mg/mL), and G4 served as the control to the vehicle; receiving molasses 8 mL/kg BW twice weekly for 6 weeks. Blood, serum, and tissue samples were collected at the middle and the end of the trial. AZ was made using the sonication sol–gel method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were performed to confirm the crystal structure, purity, particle size, and oxidation states. AZ showed immunostimulant, acaricidal, and antioxidant effects with normal tissue histological structure and low tissue residual levels. Additionally, there were improvements in blood interferon-gamma, immunoglobulin (Ig) M, IgG, phagocytic activity, phagocytic index, globulin, and total protein in the AZ group. The XRD patterns of AZ were coordinated by XRD reference codes Crystallography Open Database (COD): 9016326 for Tenorite (CuO) and by XRD reference COD: 9004179 for Zincite (ZnO). The CuO and ZnO crystal sizes were 21.87 Å and 24.89 Å, respectively. The XPS spectra indicated the presence of Cu as Cu (II) and Zn as ZnO.OH and ZnO. In conclusion, AZ exhibited antioxidant, acaricidal, and immunostimulant effects, with mild residues in the brain, liver, and kidney tissues, while maintaining a normal histological structure of tissues.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence of Potentially Zoonotic Endoparasites in Domestic Dog Puppies
by
Gisele Moraes dos Santos Reginaldo, Giovanni Widmer, Sandra Valéria Inácio, Jancarlo Ferreira Gomes, Walter Bertequini Nagata, Gabriela Pinheiro Tirado Moreno, João Alfredo Biagi Camargo Neto, Wagner Luis Ferreira, Felipe Augusto Soares and Katia Denise Saraiva Bresciani
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 332; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040332 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Despite the existence of therapeutic and prophylactic measures, gastrointestinal parasites are common in pets. Due to the zoonotic potential of some species, parasitic protozoa and helminths are of great importance to public health. In this study, we investigated the occurrence of the main
[...] Read more.
Despite the existence of therapeutic and prophylactic measures, gastrointestinal parasites are common in pets. Due to the zoonotic potential of some species, parasitic protozoa and helminths are of great importance to public health. In this study, we investigated the occurrence of the main gastrointestinal parasites in domestic dog puppies in the city of Araçatuba, São Paulo, Brazil. One hundred fecal samples were collected from dogs up to six months of age. Parasites were diagnosed using Willis’, Faust’s and malachite green coproparasitological techniques. Parasite prevalence as determined by Willis and/or Faust diagnostic techniques was as follows: Toxocara spp. 34%, Cystoisospora spp. 28%, Ancylostomatidae 22% and Giardia spp. 8%. These prevalence rates were calculated by considering an animal to be positive if Willis’ or Faust’s or both tests returned a positive result. Cryptosporidium diagnosis with malachite green was negative for all samples. Infection with Toxocara spp., the most prevalent pathogen in this survey, was not limited to dogs with abnormal fecal consistency. The occurrence of asymptomatic parasitized dogs increases the risk of zoonotic transmission.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Computed Tomography and a Dental Intraoral Scanner to Generate Three-Dimensional Models of the Beaks of Three Bird Species
by
Gabriel Corrêa de Camargo, Sheila Canevese Rahal, Reinaldo Abdala Junior, Jeana Pereira da Silva, Daniel Simões da Silva, Maria Cristina Reis Castiglioni, Ricardo Shoiti Ichikawa and Bruno Critelli Carvalho
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 331; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040331 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
This study aimed to assess the beaks of Neotropical birds using two scanning techniques—CT and a dental intraoral scanner—along with macroscopic analysis. Six specimens per family were selected, including parakeets, red-legged seriemas, and black vultures. The upper beaks were measured in the CT
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to assess the beaks of Neotropical birds using two scanning techniques—CT and a dental intraoral scanner—along with macroscopic analysis. Six specimens per family were selected, including parakeets, red-legged seriemas, and black vultures. The upper beaks were measured in the CT sagittal view for length along the longitudinal axis and height on the transverse axis. The same measurements were performed on the 3D images. Additionally, beak width in the middle of the naris area, as well as the length and height of the nares, were measured on the 3D images. The closed polygon tool outlined the beak, generating volume in cm2. The 3D images obtained with the dental scanner were measured, similarly to those from 3D-CT scans for the beaks’ length, height, and width. Macroscopic measurements of the beaks were also conducted. Some differences in beak measurements between imaging methods were verified. In conclusion, both techniques are effective, but CT provides more detailed information. The combination of both methods would be ideal for developing and applying beak prostheses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Biomedical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
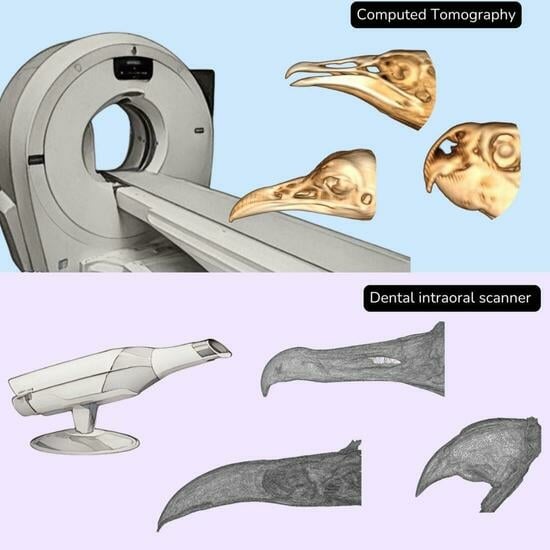
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Continuous Lipopolysaccharide Induction on Oxidative Stress and Heart Injury in Weaned Piglets
by
Jinyan Li, Guotong Zhao, Jin Liu, Xiaofen Hu, Wanting Yu, Jue Wang, Shengwei Zhong, Wenlu Zhu, Tingyu Yang, Yunxiao Zhou, Yijie Jiang, Lingna Bai, Mengyan Tu, Quan Yang and Yong Li
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 330; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040330 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
After weaning, piglets no longer consume breast milk, and their immune system is not yet fully developed. At this time, if weaned piglets are infected with E. coli, their subsequent growth will be seriously affected. In the present study, 48 healthy 28-day-old
[...] Read more.
After weaning, piglets no longer consume breast milk, and their immune system is not yet fully developed. At this time, if weaned piglets are infected with E. coli, their subsequent growth will be seriously affected. In the present study, 48 healthy 28-day-old weaned piglets (6.65 ± 1.19 kg, Duroc × Landrace × Large White) were randomly divided into an LPS group and control group. Piglets in the LPS group were intraperitoneally injected with an LPS solution (LPS was dissolved in sterile saline to form a solution of 100 μg/mL and injected at a dose of 1 mL per kilogram of body weight) for 13 consecutive days. Piglets in the control group were injected with the same volume of sterile saline. On days 1, 5, 9, and 13 of the experiment, six piglets from each group were randomly selected for dissection, the blood and heart samples were collected, and then cardiac function-related indicators were detected. A portion of the heart tissue was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and further used to make paraffin sections; then, hematoxylin–eosin (H&E) staining was performed. Masson staining was used to detect the changes in collagen fibers in the hearts. The other parts of the heart tissues were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored in a refrigerator at −80 °C for the detection of tissue antioxidant indices. The mRNA expression levels of the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway, and inflammatory cytokines in heart tissues were detected by real-time PCR. The results showed that catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) contents in the heart tissue homogenates increased significantly on days 1 and 5 in LPS-induced piglets (p < 0.01, p < 0.05), while total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) contents decreased significantly on day 5 (p < 0.05). On day 5, the contents of serum cardiac function indicators lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase isoenzymes (CK-MB), and cardiac troponin I (cTn-I) were significantly increased in LPS-induced piglets (p < 0.01). On the 1st and 5th days, the heart tissue showed obvious pathological damage, which was manifested as the disordered arrangement of myocardial fibers, depression of myocardial cells, infiltration of inflammatory factors, congestion of capillaries, and significant increase in cardiac collagen fibers. On the 1st day, the mRNA expression levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) were significantly increased in LPS-induced piglets with heart injury (p < 0.01). On the 5th day, the mRNA expression levels of the TLR4 signaling pathway [TLR4, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88), nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB)], TNF-α, and interleukin 10 (IL-10) were also significantly increased in LPS-induced piglets with heart injury (p < 0.01, p < 0.05). The mRNA expression levels of the TGF-β signaling pathway (TGF-β, Smad2, and Smad4) in cardiac fibrosis-related genes were significantly increased on days 5 and 9 (p < 0.01, p < 0.05). The mRNA expression levels of Smad3 and Smad7 in cardiac fibrosis-related genes were also significantly increased on day 9 (p < 0.01). These results indicate that oxidative stress occurs in the heart tissue of LPS-induced piglets on the 1st and 5th days, leading to cardiac tissue damage. However, on the 9th and 13th days, the degree of heart damage in the piglets was less than that on the 1st and 5th days, which may be due to the tolerance of piglets’ tissues and organs because of multiple same-dose LPS stimulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Anatomy, Histology and Pathology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Clinical Trials of Cancer Immunogene Therapies in Companion Animals: An Update (2017–2024)
by
Gerardo C. Glikin and Liliana M. E. Finocchiaro
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 329; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040329 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
This review summarizes the findings of veterinary clinical trials on immunogene therapy published between 2017 and 2024. Various tumor types, including melanoma (canine and feline), mastocytoma (canine), mammary adenocarcinoma (canine), osteosarcoma (canine), and sarcoid (equine), were treated using diverse strategies. Non-viral vectors were
[...] Read more.
This review summarizes the findings of veterinary clinical trials on immunogene therapy published between 2017 and 2024. Various tumor types, including melanoma (canine and feline), mastocytoma (canine), mammary adenocarcinoma (canine), osteosarcoma (canine), and sarcoid (equine), were treated using diverse strategies. Non-viral vectors were predominantly used to deliver genes encoding tumor-associated antigens, cytokines, or suicide enzymes. Among these non-viral methods, electrotransfer was the most commonly employed technique for introducing therapeutic genes into cells. Generally, these procedures resulted in minimal or no adverse side effects, and treated animals often showed significant improvements, such as enhanced quality of life, delayed or suppressed tumor recurrence or metastasis, and increased survival times. Some of these innovative approaches hold great potential as adjunct therapies to standard treatments. The promising outcomes from immunogene therapy studies in companion animals strongly support their application in veterinary oncology and provide valuable preclinical data (including safety assessments and proof-of-concept studies) for analogous human clinical trials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Therapy in Companion Animals)
Open AccessArticle
Pathology of Free-Living Loggerhead Turtle (Caretta caretta) Embryos on the Island of Linosa (Italy)
by
Frine Eleonora Scaglione, Matteo Cuccato, Erica Longato, Paola Pregel, Daniele Zucca, Stefano Nannarelli, Alessandra De Lucia, Marco Pilia, Elisabetta Manuali, Marco Gobbi, Enrico Bollo and Simonetta Appino
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 328; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040328 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
On the beach of Linosa Island (Italy), 43 loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta) unhatched eggs were recovered from nests, formalin-fixed and necropsied. The tissue samples were stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE), Grocott, von Kossa, periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), and Movat pentachrome stains. Histologically,
[...] Read more.
On the beach of Linosa Island (Italy), 43 loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta) unhatched eggs were recovered from nests, formalin-fixed and necropsied. The tissue samples were stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE), Grocott, von Kossa, periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), and Movat pentachrome stains. Histologically, vacuolar degeneration (100.0%) and increased numbers of melanomacrophages (18.6%) in the liver, and edema (14.0%) in the lungs were observed. Twenty-five kidneys (58.1%) showed deposition of blue amorphous material with HE staining, which also appeared PAS-positive and black with von Kossa staining, allowing a diagnosis of calcium oxalate, confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The hepatic lesions may be indicative of toxicosis, infection, or a defense mechanism. A statistically significant association between the nest position and renal oxalosis (renal calcium oxalate deposition) was observed. Renal oxalosis was probably due to the exceptionally high summer temperatures, which were statistically higher compared to the temperatures recorded in the previous two years.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Anatomy, Histology and Pathology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of Multiple Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR for Vibrio Pathogen Detection in Aquaculture
by
Binzhe Zhang, Yulie Qiu, Chenxi Shi and Jian Zhang
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 327; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040327 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Vibrio genus represents a critical group of bacterial pathogens in the marine environment globally, leading to massive mortality in the aquaculture industry. Diagnosing vibriosis, an infection caused by Vibrio species, in clinical samples poses challenges due to its non-specific clinical manifestations. In
[...] Read more.
The Vibrio genus represents a critical group of bacterial pathogens in the marine environment globally, leading to massive mortality in the aquaculture industry. Diagnosing vibriosis, an infection caused by Vibrio species, in clinical samples poses challenges due to its non-specific clinical manifestations. In this study, we developed a TaqMan probe-based multiplex real-time PCR method for the simultaneous detection and quantification of four Vibrio pathogens: Vibrio anguillarum (Va), Vibrio alginolyticus (Val), Vibrio harveyi (Vh), and Vibrio scophthalmi (Vsc). The assay targets conserved intra-species regions and specific inter-species regions using specific primers and TaqMan probes to ensure specificity. Sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the multiplex real-time PCR assay could simultaneously detect the four different bacteria, with detection limits of 26–60 copies per reaction, making it 100 times more sensitive than conventional PCR assays. Additionally, the assay exhibited high reproducibility, with intra- and inter-group coefficients of variation below 1.4%. A total of 63 clinical samples was analyzed using this established assay, which successfully detected both single and mixed infections. These results demonstrate that the multiplex quantitative PCR assay is a rapid, specific, and sensitive diagnostic tool for the detection of Va, Val, Vh, and Vsc, making it suitable for monitoring these bacteria in both single- and co-infected clinical samples.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence and Genotyping of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in Sheep from Inner Mongolia, China
by
Rong Zhang, Yue-Rong Lv, Bo Yang, Hao Wang, Jun-Tao Jia, Zhi-Hong Wu, Ming Nie, Lian-Yang Sun, Shi-Yuan Xue, Yu-Lin Ding, Rui-Bin Chen, Siqin Tunala, Li Zhao and Yong-Hong Liu
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 326; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040326 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Paratuberculosis (PTB) is a chronic wasting disease mainly caused by Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) in ruminants. It is difficult to diagnose, prevent, treat, and eradicate, thereby causing serious economic losses to the livestock industry. Therefore, finding a detection method with high sensitivity
[...] Read more.
Background: Paratuberculosis (PTB) is a chronic wasting disease mainly caused by Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) in ruminants. It is difficult to diagnose, prevent, treat, and eradicate, thereby causing serious economic losses to the livestock industry. Therefore, finding a detection method with high sensitivity and specificity is crucial to preventing and controlling PTB. Methods: A total of 1585 fresh fecal samples were collected from 12 prefectures and cities across Inner Mongolia between March 2022 and October 2024. The samples were subjected to pretreatment, followed by DNA extraction. Subsequently, MAP detection and genotyping were performed using a two-step qPCR method. Results: The overall prevalence of MAP in ovines was 3.34% (53/1585), with the prevalence in 12 prefectures and cities ranging from 0% (0/100) to 7.73% (15/194). In the eastern, central, and western regions, the prevalence rates were 4.74% (31/654), 3.68% (14/394), and 1.49% (8/537); in small-scale and intensive farms, they were 3.23% (22/682), and 3.56% (31/903); and in goats and sheep, they were 0.91% (2/219) and 4.98% (36/723), respectively. The overall prevalence rates of C- and S-type MAP were 2.90% (46/1585) and 0.44% (7/1585), respectively. Conclusions: To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to conduct an epidemiological investigation of PTB in sheep across all nine cities and three leagues in Inner Mongolia and to perform MAP typing on a large scale. It elucidated the differences in the prevalence of PTB in different regions of Inner Mongolia and found that geographical location and sheep breed are potential risk factors for the differences in MAP prevalence. Furthermore, it has been shown that C- and S-type MAP coexist in the eastern and central regions of Inner Mongolia.
Full article
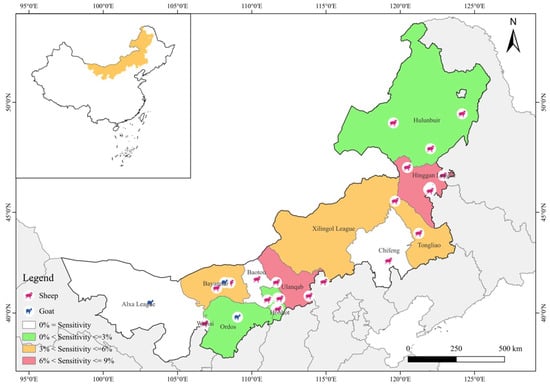
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Targeted-Amplicon NGS for Blastocystis sp. in Shepherd Dogs of Portugal Discriminates Co-Colonization with Multiple Zoonotic Subtypes
by
Sara Gomes-Gonçalves, Maria João Feiteiro, Guilherme Moreira, Rita Cruz, Fernando Esteves, Helena Vala and João R. Mesquita
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 325; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040325 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Research on endoparasites in pet dogs has been growing, but shepherd dogs have largely been overlooked. These dogs frequently share close proximity not only with sheep, which are reservoirs of zoonotic subtypes of Blastocystis, but also with their owners. This close contact
[...] Read more.
Research on endoparasites in pet dogs has been growing, but shepherd dogs have largely been overlooked. These dogs frequently share close proximity not only with sheep, which are reservoirs of zoonotic subtypes of Blastocystis, but also with their owners. This close contact increases the potential for shepherd dogs to act as intermediates in the transmission of Blastocystis. To clarify the role of these dogs as reservoirs for this parasite, this study investigated the presence of Blastocystis in shepherd dogs. Stool samples from Portuguese shepherd dogs were analyzed using SYBR-Green-based real-time PCR and melting curve analysis followed by targeted-amplicon NGS for mixed infections detection. Our results revealed a 60% occurrence of Blastocystis sp. in shepherd dog stools and frequent identification of zoonotic subtypes ST1–ST4 and ST14. Additionally, we observed mixed infections and subtype diversity within individual dogs, suggesting a potential role in cross-species transmission between livestock and humans.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Residual Black Wolfberry Fruit Improves Meat Quality of Sheep by Enhancing Immune and Antioxidant Capacity
by
Pingping Duan, Yuxia Yang, Liangzhong Hou, Ying Wu, Jinlong Li, Congbin Xu and Tongjun Guo
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 324; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040324 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
The residual black wolfberry fruit (RBWF), rich in nutrients and active substances, has the potential to serve as an antibiotic alternative. This study evaluated the concentration-dependent effects of RBWF on serum biochemistry, immunity, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality of fattening sheep. Forty 3-month-old
[...] Read more.
The residual black wolfberry fruit (RBWF), rich in nutrients and active substances, has the potential to serve as an antibiotic alternative. This study evaluated the concentration-dependent effects of RBWF on serum biochemistry, immunity, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality of fattening sheep. Forty 3-month-old sheep were randomly assigned into four groups with 10 replicates in each group and fed experimental RBWF-supplemented diets (0%, 2%, 5%, and 8%). The results showed that RBWF supplementation significantly increased the serum levels of TP, BUN, ALT, AST, IgA, IgM, T-AOC, SOD, and GSH-Px in sheep (p < 0.05), while significantly decreasing the levels of LDH, TG, LDL-c, IgG, and MDA (p < 0.05). Furthermore, dietary RBWF significantly increased the VB1 and IMP levels in the longissimus dorsi muscle of sheep (p < 0.05) and significantly decreased the contents of fat and cholesterol (p < 0.05). Finally, RBWF increased the contents of C20:4 and Glu (p < 0.05). In conclusion, dietary supplementation with RBWF can improve the immune and antioxidant capacity of sheep and has a certain effect on improving the flavor of meat, of which 5% is the best.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Health and Welfare of Farm Animals and Their Impact on the Quality and Safety of the Derived Products)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Probiotic Characterization of Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum SDN1.2 and Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Klebsiella pneumoniae-Infected Mammary Glands
by
Jia Cheng, Jingdi Tong, Can Li, Ziyan Wang, Hao Li, Meiyi Ren, Jinshang Song, Deyuan Song, Qinna Xie and Mingchao Liu
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 323; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040323 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
K. pneumoniae is a major cause of bovine mastitis worldwide, making it difficult to control due to its resistance to multiple drugs. L. paraplantarum has been explored as a promising new approach to fighting bovine mastitis. In this study, the probiotic potential and
[...] Read more.
K. pneumoniae is a major cause of bovine mastitis worldwide, making it difficult to control due to its resistance to multiple drugs. L. paraplantarum has been explored as a promising new approach to fighting bovine mastitis. In this study, the probiotic potential and safety of L. paraplantarum SDN1.2, as well as its ex vivo and in vivo anti-inflammatory effects against K. pneumoniae-induced mastitis, were comprehensively investigated using bioinformatics analyses and experimental validation methods. The results revealed that L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 exhibits non-hemolytic activity, is not cytotoxic, lacks virulence genes (e.g., adhesion factors, toxins, and invasion factors) and antibiotic resistance genes (e.g., beta-lactamases and tetracycline resistance genes), as supported by whole-genome sequencing, and significantly inhibits the growth of K. pneumoniae, as evaluated by antimicrobial tests. Following further validation in vitro, L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 demonstrated the capability to inhibit the adhesion and invasion of K. pneumoniae to bMECs. In a mouse model of K. pneumoniae-induced mastitis, L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 reduced the extent of neutrophil infiltration and inflammatory lesions. Furthermore, L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 pretreatment significantly reduced myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and the expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-a) in mouse mammary gland tissue. In K. pneumoniae-infected bMECs, L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 significantly lowered lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels and expression of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α. The results demonstrated that the newly isolated L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 from bovine sources exhibits promising characteristics as a safe probiotic for the alleviation of bovine mastitis due to its safety profile and anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ruminant Mastitis: Therapies and Control)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bats as Hosts of Antimicrobial-Resistant Mammaliicoccus lentus and Staphylococcus epidermidis with Zoonotic Relevance
by
Vanessa Silva, Manuela Caniça, Rani de la Rivière, Paulo Barros, João Alexandre Cabral, Patrícia Poeta and Gilberto Igrejas
Vet. Sci. 2025, 12(4), 322; https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040322 - 1 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bats are increasingly recognized as reservoirs for antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, playing a potential role in the dissemination of resistance genes across species and regions. In this study, 105 bats from 19 species in Portugal were sampled to investigate the presence, antimicrobial resistance, and genetic
[...] Read more.
Bats are increasingly recognized as reservoirs for antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, playing a potential role in the dissemination of resistance genes across species and regions. In this study, 105 bats from 19 species in Portugal were sampled to investigate the presence, antimicrobial resistance, and genetic characteristics of Mammaliicoccus and Staphylococcus isolates. Thirteen Mammaliicoccus lentus and Staphylococcus epidermidis were recovered. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed multidrug resistance in three isolates, with S. epidermidis carrying mph(C), msr(A), and dfrC genes, and M. lentus harboring salB, tet(K), and str. Notably, qacA was detected in S. epidermidis, highlighting its plasmid-associated potential for horizontal gene transfer to more pathogenic bacteria. Heavy metal resistance genes (arsB and cadD) were also identified, suggesting the role of environmental factors in co-selecting antimicrobial resistance. Molecular typing revealed the S. epidermidis strain as ST297, a clone associated with both healthy humans and invasive infections. These findings emphasize the need for monitoring bats as reservoirs of resistance determinants, particularly in the context of zoonotic and environmental health. The presence of mobile genetic elements and plasmids further underscores the potential for the dissemination of resistance. This study reinforces the importance of adopting a One Health approach to mitigate the risks associated with antimicrobial resistance.
Full article
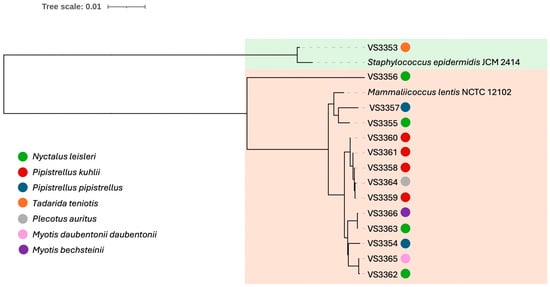
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Veterinary Sciences Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Fermentation, Microplastics, Veterinary Sciences
Livestock and Microplastics
Topic Editors: Sonia Tassone, Beniamino T. Cenci-GogaDeadline: 20 May 2025
Topic in
Animals, Antioxidants, Veterinary Sciences, Agriculture
Feeding Livestock for Health Improvement
Topic Editors: Hui Yan, Xiao XuDeadline: 30 May 2025
Topic in
Animals, Dairy, Microorganisms, Veterinary Sciences, Metabolites, Life, Parasitologia
The Complexity of Parasites in Animals: Impacts, Innovation, and Interventions
Topic Editors: Kun Li, Rongjun Wang, Ningbo Xia, Md. F. KulyarDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topic in
Animals, Fishes, Veterinary Sciences
Application of the 3Rs to Promote the Welfare of Animals Used in Scientific Research and Testing
Topic Editors: Johnny Roughan, Laura CalvilloDeadline: 20 September 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Veterinary Sciences
Round Cell Tumors of Animals
Guest Editor: Valeria MartiniDeadline: 15 April 2025
Special Issue in
Veterinary Sciences
Veterinary Forensic Pathology and Forensic Investigations in Veterinary Practice
Guest Editors: Giuseppe Piegari, Ilaria D'AquinoDeadline: 15 April 2025
Special Issue in
Veterinary Sciences
Advancements in Livestock Staphylococcus sp.
Guest Editor: Nathália Cristina Cirone SilvaDeadline: 25 April 2025
Special Issue in
Veterinary Sciences
New Insights into Companion Animal Mammary Cancer: From Diagnosis to Treatment
Guest Editors: Ana Faustino, Paula Oliveira, Rui Gil da CostaDeadline: 25 April 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Veterinary Sciences
One-Health Approach to Bee Health
Collection Editors: Giovanni Cilia, Antonio Nanetti








